A simplified and robust risk stratification model for stem cell transplantation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 39366384
- PMCID: PMC11513827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101762
A simplified and robust risk stratification model for stem cell transplantation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
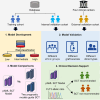
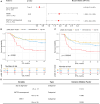
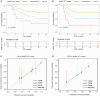
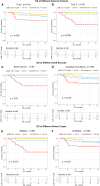
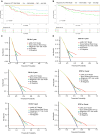
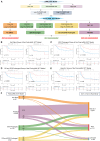
The efficacy of stem cell transplantation (SCT) in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (pAML) remains unsatisfactory due to the limitations of existing prognostic models in predicting efficacy and selecting suitable candidates. This study aims to develop a cytomolecular risk stratification-independent prognostic model for SCT in pAML patients at CR1 stage. The pAML SCT model, based on age, KMT2A rearrangement (KMT2A-r), and minimal residual disease at end of course 1 (MRD1), effectively classifies patients into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups. We validate the effectiveness in an internal validation cohort and in four external validation cohorts, consisting of different graft sources and donors. Moreover, by incorporating the FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3/internal tandem duplication (FLT3/ITD) allelic ratio, the pAML SCT model is refined, enhancing its ability to effectively select suitable candidates. We develop a simple and robust risk stratification model for pAML patients undergoing SCT, to aid in risk stratification and inform pretransplant decision-making at CR1 stage.
Keywords: allelic ratio of FLT3/ITD; minimal residual disease; pediatric acute myeloid leukemia; risk stratification model; stem cell transplantation.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pollard J.A., Guest E., Alonzo T.A., Gerbing R.B., Loken M.R., Brodersen L.E., Kolb E.A., Aplenc R., Meshinchi S., Raimondi S.C., et al. Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin Improves Event-Free Survival and Reduces Relapse in Pediatric KMT2A-Rearranged AML: Results From the Phase III Children's Oncology Group Trial AAML0531. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021;39:3149–3160. doi: 10.1200/jco.20.03048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

