Evolution of the conformational dynamics of the molecular chaperone Hsp90
- PMID: 39366960
- PMCID: PMC11452706
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52995-y
Evolution of the conformational dynamics of the molecular chaperone Hsp90
Abstract
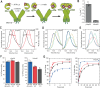
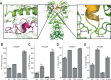
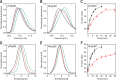
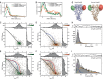
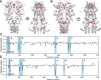
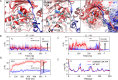
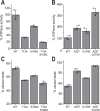
Hsp90 is a molecular chaperone of central importance for protein homeostasis in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells, with key functional and structural traits conserved from yeast to man. During evolution, Hsp90 has gained additional functional importance, leading to an increased number of interacting co-chaperones and client proteins. Here, we show that the overall conformational transitions coupled to the ATPase cycle of Hsp90 are conserved from yeast to humans, but cycle timing as well as the dynamics are significantly altered. In contrast to yeast Hsp90, the human Hsp90 is characterized by broad ensembles of conformational states, irrespective of the absence or presence of ATP. The differences in the ATPase rate and conformational transitions between yeast and human Hsp90 are based on two residues in otherwise conserved structural elements that are involved in triggering structural changes in response to ATP binding. The exchange of these two mutations allows swapping of the ATPase rate and of the conformational transitions between human and yeast Hsp90. Our combined results show that Hsp90 evolved to a protein with increased conformational dynamics that populates ensembles of different states with strong preferences for the N-terminally open, client-accepting states.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Richter, K., Haslbeck, M. & Buchner, J. The heat shock response: life on the verge of death. Mol. Cell40, 253–266 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Karagoz, G. E. & Rudiger, S. G. Hsp90 interaction with clients. Trends Biochem. Sci.40, 117–125 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Zhao, R. et al. Navigating the chaperone network: an integrative map of physical and genetic interactions mediated by the hsp90 chaperone. Cell120, 715–727 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

