Quercetin as a therapeutic agent activate the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway to alleviate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 39367100
- PMCID: PMC11452703
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73075-7
Quercetin as a therapeutic agent activate the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway to alleviate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
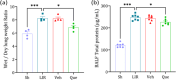
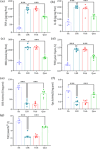
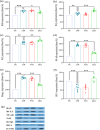
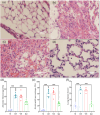
Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury (LIRI) causes oxidative stress, inflammation, and immune system activation. The Nrf2/Keap1/HO-1 pathway is important in cellular defense against these effects. Quercetin, a flavonoid with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties, has been investigated. Our aim in this study was to investigate the effect of quercetin on preventing lung ischemia-reperfusion injury and the role of the Nrf2/Keap1/HO-1 pathway. Sixty-four male Wistar rats were divided into four distinct groups(n = 16). Sham, lung ischemia-reperfusion (LIR), Saline + LIR, Quercetin + LIR (30 mg/kg i.p for a week before LIR). LIR groups were subjected to 60 min of ischemia (left pulmonary artery, vein, and bronchus) and 120 min of reperfusion. Our assessment encompassed a comprehensive analysis of various factors, including the evaluation of expression Nrf2, Keap1, and Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) levels and NF-κB protein. Furthermore, we examined markers related to inflammation (interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor alpha), oxidative stress (malondialdehyde, total oxidant status, superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, total antioxidant capacity), lung edema (Wet/dry lung weight ratio and total protein concentration), apoptosis (Bax and Bcl2 protein), and histopathological alterations (intra-alveolar edema, alveolar hemorrhage, and neutrophil infiltration). Our results show that ischemia-reperfusion results in heightened inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, lung edema, and histopathological damage. Quercetin showed preventive effects by reducing these markers, acting through modulation of the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. This anti-inflammatory effect, complementary to the antioxidant effects of quercetin, provides a multifaceted approach to cell protection that is important for developing therapeutic strategies against ischemia-reperfusion injury and could be helpful in preventive strategies against ischemia-reperfusion.
Keywords: Inflammation; Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury; Nrf2/Keap1 pathway; Oxidative stress; Quercetin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ambrosio, G. & Tritto, I. Reperfusion injury: experimental evidence and clinical implications. Am. Heart J. 138, S69–S75 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Ng, C. S., Wan, S., Yim, A. P. & Arifi, A. A. Pulmonary dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Chest 121, 1269–1277 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Christie, J. D. et al. Report of the ISHLT working group on primary lung graft dysfunction part II: definition. A consensus statement of the international society for heart and lung transplantation. J. Heart lung Transplant. 24, 1454–1459 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Pak, O. et al. Lung ischaemia–reperfusion injury: the role of reactive oxygen species. Pulm. Vasc. Redox Signal. Health Dis. 195–225 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

