State-of-the-art application of nanoparticles in radiotherapy: a platform for synergistic effects in cancer treatment
- PMID: 39367110
- PMCID: PMC12119707
- DOI: 10.1007/s00066-024-02301-y
State-of-the-art application of nanoparticles in radiotherapy: a platform for synergistic effects in cancer treatment
Abstract
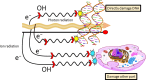
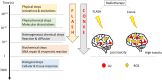
Radiotherapy (RT) is a gold standard cancer treatment worldwide. However, RT has limitations and many side effects. Nanoparticles (NPs) have exclusive properties that allow them to be used in cancer therapy. Consequently, the combination of NP and RT opens up a new frontier in cancer treatment. Among NPs, gold nanoparticles (GNPs) are the most extensively studied and are considered ideal radiosensitizers for radiotherapy due to their unique physicochemical properties and high X‑ray absorption. This review analyzes the various roles of NPs as radiosensitizers in radiotherapy of glioblastoma (GBS), prostate cancer, and breast cancer and summarizes recent advances. Furthermore, the underlying mechanisms of NP radiosensitization, including physical, chemical, and biological mechanisms, are discussed, which may provide new directions for next-generation GNP optimization and clinical transformation.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Glioblastoma (GBS); Nanoparticles (NPs); Prostate cancer (PCa); Radiotherapy (RT).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M. Mostafavi, F. Ghazi, M. Mehrabifard, V. Alivirdiloo, M. Hajiabbasi, F. Rahimi, A. Mobed, G. Taheripak, M. Ramezani Farani, Y.S. Huh, S. Bakhtiyari, and I. Alipourfard declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Chhikara BS, Parang K (2023) Global cancer statistics 2022: the trends projection analysis, chemical. Biol Lett 10(1):451–451
-
- Shakil MS, Mahmud KM, Sayem M, Niloy MS, Halder SK, Hossen MS, Uddin MF, Hasan MA (2021) Using chitosan or chitosan derivatives in cancer therapy. Polysaccharides 2(4):795–816 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

