Profibrotic monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages are expanded in patients with persistent respiratory symptoms and radiographic abnormalities after COVID-19
- PMID: 39367123
- PMCID: PMC11519004
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-01975-x
Profibrotic monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages are expanded in patients with persistent respiratory symptoms and radiographic abnormalities after COVID-19
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Profibrotic monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages are expanded in patients with persistent respiratory symptoms and radiographic abnormalities after COVID-19.Nat Immunol. 2025 Feb;26(2):323. doi: 10.1038/s41590-025-02076-z. Nat Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39774409 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
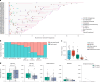
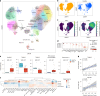
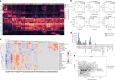
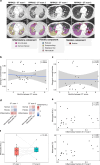
Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages drive lung injury and fibrosis in murine models and are associated with pulmonary fibrosis in humans. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages have been suggested to develop a phenotype that promotes lung repair as injury resolves. We compared single-cell and cytokine profiling of the alveolar space in a cohort of 35 patients with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 who had persistent respiratory symptoms and abnormalities on a computed tomography scan of the chest that subsequently improved or progressed. The abundance of monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages, their gene expression programs, and the level of the monocyte chemokine CCL2 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid positively associated with the severity of radiographic fibrosis. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages from patients with resolving or progressive fibrosis expressed the same set of profibrotic genes. Our findings argue against a distinct reparative phenotype in monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages, highlighting their utility as a biomarker of failed lung repair and a potential target for therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.R.W. reports consultancy agreements and advisory boards with AstraZeneca, Intellia Therapeutics, Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Regeneron and Verona Pharma and has received grant support from the NIH, Department of Defense and Boehringer Ingelheim. He is a cofounder and equity shareholder in Quantitative Imaging Solutions, a company that provides consulting services for image and data analytics. G.R.W.’s spouse works for Biogen. Raul S.J.E. received contracts to serve as the Image Core for studies funded by Lung Biotechnology, Insmed and Gossamer Bio. He has a Sponsored Research Agreement with Boehringer Ingelheim and has served as a consultant for Leuko Labs and Mount Sinai. He is a cofounder and equity shareholder in Quantitative Imaging Solutions. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HL147575/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL116931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL076139/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R21 LM013670/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL154998/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL147290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES028829/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- I01 CX001777/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- P01AG049665/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 ES034350/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068579/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES027574/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U19 AI181102/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI135964/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- DMS-1547394/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- R21 AG075423/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD011996/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 1F31AG071225/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 ES027574/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG068579/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 597491-RWC01/Simons Foundation
- R01 HL153312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 24PRE1196998/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)
- U54 AG079754/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL145478/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL158139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL154998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI181102/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01HL116931/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R21LM013670/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL173987/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL153312/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01ES034350/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL145478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147575/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES028829/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL173987/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 1764421-01/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- F31 AG071225/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR001422/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P01 HL169188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL158139/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R21AG075423/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01HL147290/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P01 HL114501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL176632/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL076139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54AG079754/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

