Regulation of voltage-gated sodium channels by TNF-α during herpes simplex virus latency establishment
- PMID: 39367281
- PMCID: PMC11998310
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-024-01229-4
Regulation of voltage-gated sodium channels by TNF-α during herpes simplex virus latency establishment
Abstract
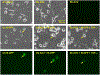
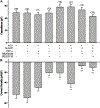
During lytic or latent infection of sensory neurons with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) there are significant changes in the expression of voltage-gated Na+ channels, which may disrupt the transmission of pain information. HSV-1 infection can also evoke the secretion of various pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6. In this work, we hypothesized that TNF-α regulates the expression of Na+ channels during HSV-1 latency establishment in ND7/23 sensory-like neurons. Latency establishment was mimicked by culturing HSV-1 infected ND7/23 cells in the presence of acyclovir (ACV) for 3 days. Changes in the functional expression of voltage-gated Na+ channels were assessed by whole-cell recordings. Our results demonstrate that infection of ND7/23 cells with the HSV-1 strain McKrae with GFP expression (M-GFP) causes a significant decrease in sodium currents during latency establishment. Exposure of ND7/23 cells to TNF-α during latency establishment reverses the effect of HSV-1, resulting in a significant increase in sodium current density. However, Na+ currents were not restored by 3 day-treatment with IL-6. There were no changes in the pharmacological and biophysical properties of sodium currents promoted by TNF-α, including sensitivity to tetrodotoxin and the current-voltage relationship. TNF-α stimulation of ND7/23 cells increases p38 signaling. Inhibition of p38 signaling with SB203580 or SB202190 eliminates the stimulatory effect of TNF-α on sodium currents. These results indicate that TNF-α signaling in sensory neurons during latency establishment upregulates the expression of voltage-gated Na+ channels in order to maintain the transmission of pain information.
Keywords: Electrical excitability; Pain; Sensory neuron; Sodium channel; Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to The Journal of NeuroVirology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest regarding the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

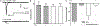


Similar articles
-
Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Activity in Human Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons by Herpesvirus Quiescent Infection.J Virol. 2020 Jan 17;94(3):e01823-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01823-19. Print 2020 Jan 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31694955 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of T-type Ca2+ channel expression by interleukin-6 in sensory-like ND7/23 cells post-herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) infection.J Neurochem. 2019 Oct;151(2):238-254. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14697. Epub 2019 May 15. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 30888683 Free PMC article.
-
IFNβ absence compensates for LAT functions in latency reactivation and T cell exhaustion.J Virol. 2025 Jun 17;99(6):e0037425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00374-25. Epub 2025 May 12. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40353667 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for men and women with their first episode of genital herpes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 30;2016(8):CD010684. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010684.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27575957 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for prevention of herpes simplex labialis (cold sores on the lips).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Aug 7;2015(8):CD010095. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010095.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26252373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andoh T, Shiraki K, Kurokawa M (1995) Paresthesia induced by cutaneous infection with herpes simplex virus in rats. Neurosci Lett 190(2):101–104 - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Pang RP, Shen KF, Zimmermann M, Xin WJ, Li YY, Liu XG (2011) TNF-α enhances the currents of voltage gated sodium channels in uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons following motor nerve injury. Exp Neurol 227(2):279–286 - PubMed
-
- Czeschik JC, Hagenacker T, Schäfers M, Büsselberg D (2008) TNF-alpha differentially modulates ion channels of nociceptive neurons. Neurosci Lett 434(3):293–298 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

