Sacral neuromodulation for Organophosphate-induced delayed neuropathy neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: a case report
- PMID: 39367402
- PMCID: PMC11451249
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-024-01600-x
Sacral neuromodulation for Organophosphate-induced delayed neuropathy neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: a case report
Abstract
Background: Organophosphate-Induced Delayed Neuropathy (OPIDN) is a rare neurological disorder triggered by exposure to organophosphorus compounds. These compounds exert their neurotoxic effects by impacting the nervous system, leading to systemic manifestations. Urinary system symptoms are infrequently observed in clinical settings. Currently, effective therapeutic interventions for OPIDN-related urinary symptoms are lacking. Sacral nerve modulation therapy, an FDA-approved approach for managing lower urinary tract symptoms, presents as a promising option. Herein, we present a case of OPIDN-induced lower urinary tract obstruction successfully treated with sacral nerve modulation therapy, resulting in substantial symptom relief.
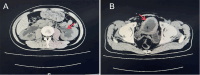
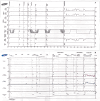
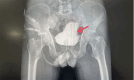
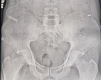
Case report: A 27-year-old male patient presented with severe bilateral hydronephrosis, attributed to low bladder compliance and accompanied by a fever persisting for 6 days. The patient's medical history revealed accidental ingestion of organophosphate pesticide (Dimethoate) with no concomitant underlying diseases. In consideration of the potential for OPIDN, surgical intervention in the form of sacral neuromodulation (phase I) was undertaken. Subsequent evaluation one month post-surgery revealed notable improvements in both bladder compliance and bilateral hydronephrosis, necessitating sacral neuromodulation (phase II). Presently, following a 5-month follow-up period, the patient remains asymptomatic and in favorable health.
Conclusion: This patient achieved long-term relief using sacral neuromodulation.
Keywords: Neurogenic bladder; Organophosphate-induced delayed neuropathy (OPIDN); Organophosphorus compounds; Peripheral nerve axons; Sacral neuromodulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

