Insights and networks: methodological assessment and scientometric analysis of economic evaluations in dentistry
- PMID: 39367462
- PMCID: PMC11451011
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-11668-8
Insights and networks: methodological assessment and scientometric analysis of economic evaluations in dentistry
Abstract
Introduction: Assessing the methodological quality of economic evaluations (EEs) is crucial for evidence-based decision-making. The study aimed to evaluate EEs in restorative dentistry and endodontics, while also analyzing the scientific landscape of researchers and publications through co-authorship and citation network analysis providing an insight into the distribution of scientific expertise.
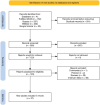
Methodology: A systematic search for relevant articles from 2012 to 2022 was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and EBSCO. The ten-point Drummond checklist was used to appraise the methodological quality of included studies. Bibliometric data for network analysis were extracted from the Dimensions database and visualized using VOSviewer software.
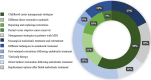
Results: Of the 37 articles, 81.08% scored good, 16.21% average, and 2.7% poor on the methodological rating scale. Most of the included studies were in Q1 journals, with limited representation in Q2 and Q3 journals. Compliance was highest in Q2 journals (95%), followed by Q1 (88.36%), while it dropped to 40% for Q3 journals. Co-authorship analysis revealed a dense network of researchers, with Prof. Falk Schwendicke V. having a significant influence. Moreover, the Journal of Dentistry had the highest impact, followed by Journal of Endodontics and BMC Oral Health.
Conclusions: Despite a diverse scientific landscape, participation from developing countries was limited emphasizing the need for inclusivity and diversity in the scientific network. While the quantity of good-quality studies was encouraging, the overall quality of evidence remains paramount for decision-making in healthcare policy and practice. Therefore, continuous efforts to improve methodological rigor and reporting practices are essential to contribute robust evidence.
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness analysis; Economic evaluation; Endodontics (MeSH terms); Health economics; Healthcare Economics; Restorative Dentistry.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Naved N, Umer F, Khowaja AR. Cost-effectiveness analysis of regenerative endodontics versus MTA apexification. JDR Clin Trans Res. 2024;9(3):231-238. - PubMed
-
- Vernazza C, Heasman P, Gaunt F, Pennington M. How to measure the cost-effectiveness of periodontal treatments. Periodontol 2000. 2012;60(1):138–46. - PubMed
-
- Sanders GD, Neumann PJ, Basu A, Brock DW, Feeny D, Krahn M, et al. Recommendations for conduct, methodological practices, and reporting of cost-effectiveness analyses: second panel on cost-effectiveness in Health and Medicine. JAMA. 2016;316(10):1093–103. - PubMed
-
- Blackmore CC, Smith WJ. Economic analyses of radiological procedures: a methodological evaluation of the medical literature. Eur J Radiol. 1998;27(2):123–30. - PubMed
-
- Schwendicke F, Herbst SR. Health economic evaluation of endodontic therapies. Int Endod J. 2023;56(Suppl 2):207–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

