Long term outcomes and risk factors of compensatory hyperhidrosis after thoracoscopic sympathectomy in primary palmar hyperhidrosis patients: a retrospective single-center study
- PMID: 39367483
- PMCID: PMC11451246
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-03086-y
Long term outcomes and risk factors of compensatory hyperhidrosis after thoracoscopic sympathectomy in primary palmar hyperhidrosis patients: a retrospective single-center study
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the long-term outcomes of compensatory hyperhidrosis (CH) after thoracoscopic sympathectomy and explore the risk factors affecting postoperative CH in primary palmar hyperhidrosis(PPH) patients.
Method: A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients who underwent thoracoscopic sympathectomy in the thoracic surgery department of our hospital from January 2015 to May 2022. Long-term follow-up surveys was conducted to collect data on post-operative satisfaction, PPH recurrence, and CH occurrence. Postoperative CH outcomes were assessed using the HDSS and satisfaction scores scale. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify independent risk factors for postoperative CH.
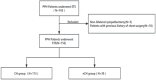
Result: A total of 152 patients was included in the final study, with 113 cases in the CH group and 39 cases in the nCH group. The incidence of postoperative CH was 74.3% (113/152), within which 33.6% (38/113) were severe CH. The median follow-up time was 3.1 years(2.5-5.5y) and the median interval of CH onset after surgery was 30 days (14-90d). Univariate analysis showed that body mass index(BMI), surgical time, and transected nerve level are correlated with CH, with statistically significant differences. Multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated a higher BMI (OR = 0.864, 95% CI 0.755-0.989, P < 0.05) is the independent risk factor for the occurrence of CH. There was no statistically significant difference in HDSS scores among CH patients at 1 month, 1 year, and 3 years after surgery.
Conclusion: A higher BMI is the independent risk factor for postoperative CH after thoracoscopic sympathectomy. The incidence and severity of postoperative CH kept stable during a long term follow up.
Keywords: Body mass index; Compensatory hyperhidrosis; Primary palmar hyperhidrosis; Thoracoscopic sympathectomy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single-center experience of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis with long-term postoperative questionnaire survey.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2024 Nov;72(11):732-737. doi: 10.1007/s11748-024-02034-w. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2024. PMID: 38676901 Free PMC article.
-
Single-port Thoracoscopic Laser Sympathicotomy for Primary Hyperhidrosis: A Safe and Minimally Invasive Approach With Favorable Short-term Outcomes.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2025 Feb 1;35(1):e1340. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000001340. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2025. PMID: 39523766
-
Fifteen Years' Experience of Thoracoscopic Sympathetic Chain Interruption for Palmar Hyperhidrosis in Children and Adolescents: Evaluation of Different Techniques.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2024 Oct;34(10):941-947. doi: 10.1089/lap.2024.0026. Epub 2024 Apr 5. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2024. PMID: 38577902
-
Which patients are more likely to experience compensatory hyperhidrosis after endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy: a meta-analysis and systematic review.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 18;13:e19097. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19097. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40124609 Free PMC article.
-
Video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: results in 102 cases.Ann Vasc Surg. 2002 Nov;16(6):708-13. doi: 10.1007/s10016-001-0312-4. Epub 2002 Nov 7. Ann Vasc Surg. 2002. PMID: 12417930 Review.
Cited by
-
20-Year Efficacy of Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy for Primary Hyperhidrosis: A Cohort Study.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 8;14(14):4831. doi: 10.3390/jcm14144831. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Turhan K, Kavurmaci O, Akcam TI, Ergonul AG, Ozdil A, Cakan A, Cagirici U. Long-term outcomes and course of compensatory sweating after endoscopic sympathicotomy. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022;70(2):167–72. - PubMed
-
- Horslen LC, Wilshire CL, Louie BE, Vallières E. Long-term impact of endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;106(4):1008–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

