Mitochondrial dysfunction, cause or consequence in neurodegenerative diseases?
- PMID: 39367555
- PMCID: PMC11662158
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.202400023
Mitochondrial dysfunction, cause or consequence in neurodegenerative diseases?
Abstract
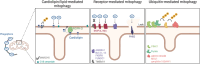
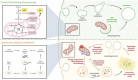
Neurodegenerative diseases encompass a spectrum of conditions characterized by the gradual deterioration of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous system. While their origins are multifaceted, emerging data underscore the pivotal role of impaired mitochondrial functions and endolysosomal homeostasis to the onset and progression of pathology. This article explores whether mitochondrial dysfunctions act as causal factors or are intricately linked to the decline in endolysosomal function. As research delves deeper into the genetics of neurodegenerative diseases, an increasing number of risk loci and genes associated with the regulation of endolysosomal and autophagy functions are being identified, arguing for a downstream impact on mitochondrial health. Our hypothesis centers on the notion that disturbances in endolysosomal processes may propagate to other organelles, including mitochondria, through disrupted inter-organellar communication. We discuss these views in the context of major neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, and their relevance to potential therapeutic avenues.
Keywords: lysosomal homeostasis; mitochondrial homeostasis; neurodegenerative diseases.
© 2024 The Author(s). BioEssays published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Van Acker, Z. P. , Luyckx, E. , & Dewilde, S. (2018). Neuroglobin expression in the brain: A story of tissue homeostasis preservation. Molecular Neurobiology, 56, 2101–2122. - PubMed
-
- Rizzollo, F. , More, S. , Vangheluwe, P. , & Agostinis, P. (2021). The lysosome as a master regulator of iron metabolism. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 46, 960–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

