SENP1 mediates zinc-induced ZnT6 deSUMOylation at Lys-409 involved in the regulation of zinc metabolism in Golgi apparatus
- PMID: 39367979
- PMCID: PMC11455790
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05452-4
SENP1 mediates zinc-induced ZnT6 deSUMOylation at Lys-409 involved in the regulation of zinc metabolism in Golgi apparatus
Abstract
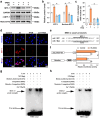
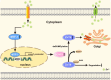
Zinc (Zn) transporters contribute to the maintenance of intracellular Zn homeostasis in vertebrate, whose activity and function are modulated by post-translational modification. However, the function of small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMOylation) in Zn metabolism remains elusive. Here, compared with low Zn group, a high-Zn diet significantly increases hepatic Zn content and upregulates the expression of metal-response element-binding transcription factor-1 (MTF-1), Zn transporter 6 (ZnT6) and deSUMOylation enzymes (SENP1, SENP2, and SENP6), but inhibits the expression of SUMO proteins and the E1, E2, and E3 enzymes. Mechanistically, Zn triggers the activation of the MTF-1/SENP1 pathway, resulting in the reduction of ZnT6 SUMOylation at Lys 409 by small ubiquitin-like modifier 1 (SUMO1), and promoting the deSUMOylation process mediated by SENP1. SUMOylation modification of ZnT6 has no influence on its localization but reduces its protein stability. Importantly, deSUMOylation of ZnT6 is crucial for controlling Zn export from the cytosols into the Golgi apparatus. In conclusion, for the first time, we elucidate a novel mechanism by which SUMO1-catalyzed SUMOylation and SENP1-mediated deSUMOylation of ZnT6 orchestrate the regulation of Zn metabolism within the Golgi apparatus.
Keywords: MTF-1; SENP1; SUMOylation; Zinc; Zinc transporter; Zn homeostasis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors disclosed no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

