Association between dynapenic abdominal obesity and arthritis among the middle-aged and older Chinese: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 39367987
- PMCID: PMC11455664
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-024-02847-y
Association between dynapenic abdominal obesity and arthritis among the middle-aged and older Chinese: a longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess the longitudinal association between dynapenic abdominal obesity and new-onset arthritis among the middle-aged and older Chinese population.
Methods: We included 6863 participants from the 2011 and 2015 waves of the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Dynapenia was defined as handgrip strength < 28 kg for males, and < 18 kg for females. Abdominal obesity was defined as a waist circumference ≥ 90 cm for males and ≥ 85 cm for females. Based on the definitions, all participants were divided into four groups: no dynapenia and no abdominal obesity (ND/NAO), abdominal obesity alone (ND/AO), dynapenia alone (D/NAO), and dynapenia and abdominal obesity (D/AO). The association between dynapenic abdominal obesity and new-onset arthritis was assessed by sex using the Poisson regression models.
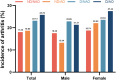
Results: After a four-year follow-up, 1272 (18.53%) participants reported new-onset arthritis. Those in the D/AO group had a significantly increased risk of new-onset arthritis compared to those in the ND/NAO group (adjusted relative risk (RR): 1.34, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.01-1.77). In females, the ND/AO (RR: 1.21, 95% CI: 1.03-1.43) and D/AO (RR: 1.39, 95% CI: 1.01-1.93) groups were associated with a higher risk of arthritis. This significant association was not observed in males.
Conclusions: Our results indicated that the combined effect of dynapenia and abdominal obesity significantly increased the risk of new-onset arthritis in females, but this association was not observed in males.
Keywords: Abdominal obesity; Arthritis; CHARLS; Dynapenia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynapenic abdominal obesity and incident functional disability: Results from a nationwide longitudinal study of middle-aged and older adults in China.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024 Aug;123:105434. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2024.105434. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38583265
-
Associations of Dynapenic Abdominal Obesity and Frailty Progression: Evidence from Two Nationwide Cohorts.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 13;16(4):518. doi: 10.3390/nu16040518. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398843 Free PMC article.
-
Dynapenic abdominal obesity and the effect on long-term gait speed and falls in older adults.Clin Nutr. 2022 Jan;41(1):91-96. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.11.011. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34864458
-
The Relationship between Dynapenic Abdominal Obesity and Fall: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 15,506 Middle to Older Adults.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 23;12(23):7253. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237253. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38068305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynapenic Abdominal Obesity and Adverse Health Effects in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;13(8):916. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13080916. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281865 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynapenic abdominal obesity and the risks of heart disease and all-cause mortality: a 7-year longitudinal study among middle-aged and older Chinese adults.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jul 16;25(1):2470. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23664-6. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40670948 Free PMC article.
-
Physical multimorbidity and dynapenic abdominal obesity among older adults from low- and middle-income countries.Commun Med (Lond). 2025 Jul 29;5(1):315. doi: 10.1038/s43856-025-01037-9. Commun Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40731163 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity: pathophysiology and therapeutic interventions.Mol Biomed. 2025 Apr 25;6(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s43556-025-00264-9. Mol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40278960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Dynapenic abdominal obesity and fall risk among older adults: a longitudinal study in Birjand.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025 Jun 28;37(1):201. doi: 10.1007/s40520-025-03092-7. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025. PMID: 40580265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Furner SE, Hootman JM, Helmick CG, Bolen J, Zack MM (2011) Health-related quality of life of US adults with arthritis: analysis of data from the behavioral risk factor surveillance system, 2003, 2005, and 2007. Arthritis Care Res 63(6):788–799 - PubMed
-
- Murphy LB, Cisternas MG, Pasta DJ, Helmick CG, Yelin EH (2018) Medical expenditures and earnings losses among US adults with arthritis in 2013. Arthritis Care Res 70(6):869–876 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

