Application of preoperative MRI lesion identification algorithm in pediatric and young adult focal cortical dysplasia-related epilepsy
- PMID: 39368329
- PMCID: PMC11540716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.seizure.2024.09.024
Application of preoperative MRI lesion identification algorithm in pediatric and young adult focal cortical dysplasia-related epilepsy
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the performance and generalizability of an automated, interpretable surface-based MRI classifier for the detection of focal cortical dysplasia.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort incorporating MRIs from the epilepsy surgery (FCD and MRI-negative) and neuroimaging (healthy controls) databases at Children's National Hospital (CNH), and a publicly-available FCD Type II dataset from Bonn, Germany. Clinical characteristics and outcomes were abstracted from patient records and/or existing databases. Subjects were included if they had 3T epilepsy-protocol MRI. Manually-segmented FCD masks were compared to the automated masks generated by the Multi-centre Epilepsy Lesion Detection (MELD) FCD detection algorithm. Sensitivity/specificity were calculated.
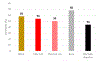
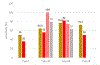
Results: From CNH, 39 FCD pharmacoresistant epilepsy (PRE) patients, 19 healthy controls, and 19 MRI-negative patients were included. From Bonn, 85 FCD Type II were included, of which 68 passed preprocessing. MELD had varying performance (sensitivity) in these datasets: CNH FCD-PRE (54 %); Bonn (68 %); MRI-negative (44 %). In multivariate regression, FCD Type IIB pathology predicted higher chance of MELD automated lesion detection. All four patients who underwent resection/ablation of MELD-identified clusters achieved Engel I outcome.
Significance: We validate the performance of MELD automated, interpretable FCD classifier in a diverse pediatric cohort with FCD-PRE. We also demonstrate the classifier has relatively good performance in an independent FCD Type II cohort with pediatric-onset epilepsy, as well as simulated real-world value in a pediatric population with MRI-negative PRE.
Keywords: Automated MRI segmentation; Automated detection; Focal cortical dysplasia; Machine learning; Non-lesional focal epilepsy; Structural MRI.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Najm I, Lal D, Alonso Vanegas M, Cendes F, Lopes-Cendes I, Palmini A, Paglioli E, Sarnat HB, Walsh CA, Wiebe S, Aronica E, Baulac S, Coras R, Kobow K, Cross JH, Garbelli R, Holthausen H, Rössler K, Thom M, El-Osta A, Lee JH, Miyata H, Guerrini R, Piao YS, Zhou D and Blümcke I The ILAE consensus classification of focal cortical dysplasia: An update proposed by an ad hoc task force of the ILAE diagnostic methods commission. Epilepsia 2022; 63:1899–1919. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Téllez-Zenteno JF, Hernández Ronquillo L, Moien-Afshari F and Wiebe S Surgical outcomes in lesional and non-lesional epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res 2010; 89:310–318. - PubMed
-
- Wang I, Oh S, Blümcke I, Coras R, Krishnan B, Kim S, McBride A, Grinenko O, Lin Y, Overmyer M, Aung TT, Lowe M, Larvie M, Alexopoulos AV, Bingaman W, Gonzalez-Martinez JA, Najm I and Jones SE Value of 7T MRI and post-processing in patients with nonlesional 3T MRI undergoing epilepsy presurgical evaluation. Epilepsia 2020; 61:2509–2520. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang ZI, Alexopoulos AV, Jones SE, Jaisani Z, Najm IM and Prayson RA The pathology of magnetic-resonance-imaging-negative epilepsy. Mod Pathol 2013; 26:1051–1058. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

