The VLDLR entry receptor is required for the pathogenesis of multiple encephalitic alphaviruses
- PMID: 39369384
- PMCID: PMC11568480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114809
The VLDLR entry receptor is required for the pathogenesis of multiple encephalitic alphaviruses
Abstract
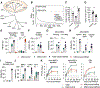
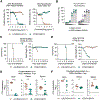
The very-low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) has been reported as an entry receptor for Semliki Forest (SFV) and Eastern equine encephalitis (EEEV) alphaviruses in cell cultures. However, the role of VLDLR in alphavirus pathogenesis and the extent to which other alphaviruses can engage VLDLR remains unclear. Here, using a surface protein-targeted CRISPR-Cas9 screen, we identify VLDLR as a receptor for Western equine encephalitis virus (WEEV) and demonstrate that it promotes the infection of multiple viruses in the WEE antigenic complex. In vivo studies show that the pathogenicity of WEEV, EEEV, and SFV, but not the distantly related Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus, is markedly diminished in VLDLR-deficient mice and that mice treated with a soluble VLDLR-Fc decoy molecule are protected against disease. Overall, these results expand our understanding of the role of VLDLR in alphavirus pathogenesis and provide a potential path for developing countermeasures against alphaviruses from different antigenic complexes.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; CP: Microbiology; Receptor; alphavirus; decoy; pathogenesis; therapy; tropism.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.S.D. is a consultant to or on the scientific advisory board for Inbios, IntegerBio, Akagera Medicines, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline, and Moderna. The Diamond laboratory has received unrelated funding support in sponsored research agreements from Emergent BioSolutions, Moderna, IntegerBio, and Vir Biotechnology. D.H.F. is a founder of Courier Therapeutics and has received unrelated funding support from Emergent BioSolutions and Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
Figures


References
-
- Reeves WC, Hutson GA, Bellamy RE, and Scrivani RP (1958). Chronic latent infections of birds with Western equine encephalomyelitis virus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med 97, 733–736. - PubMed
-
- Deresiewicz RL, Thaler SJ, Hsu L, and Zamani AA (1997). Clinical and Neuroradiographic Manifestations of Eastern Equine Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med 336, 1867–1874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

