The PIK3CA gene and its pivotal role in tumor tropism of triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 39369580
- PMCID: PMC11491976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102140
The PIK3CA gene and its pivotal role in tumor tropism of triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
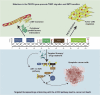
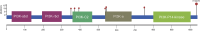
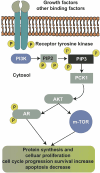
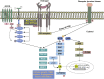
The PIK3CA gene is a linchpin in the intricate molecular network governing triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) tumor tropism, serving as a focal point for understanding this aggressive disease. Anchored within the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis, PIK3CA mutations exert substantial influence, driving cellular processes that highlight the unique biology of TNBC. This review meticulously highlights the association between PIK3CA mutations and distinct TNBC subtypes, elucidating the gene's multifaceted contributions to tumor tropism. Molecular dissection reveals how PIK3CA mutations dynamically modulate chemokine responses, growth factor signaling, and extracellular matrix interactions, orchestrating the complex migratory behaviour characteristic of TNBC cells. A detailed exploration of PIK3CA-targeted strategies in the therapeutic arena is presented, outlining the current landscape of clinical trials and precision medicine approaches. As the scientific narrative converges, this review underscores the critical role of PIK3CA in shaping the molecular intricacies of TNBC tumor tropism and illuminates pathways toward tailored interventions, promising a paradigm shift in the clinical management of TNBC.
Keywords: EMT; Metastasis; PI3K; PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway; Targeted therapy; Triple negative breast cancer; Tumor tropism.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PIK3CA mutation confers resistance to chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting apoptosis and activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Mar;9(5):410. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-698. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33842631 Free PMC article.
-
Response to mTOR and PI3K inhibitors in enzalutamide-resistant luminal androgen receptor triple-negative breast cancer patient-derived xenografts.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 1;10(4):1531-1543. doi: 10.7150/thno.36182. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32042320 Free PMC article.
-
PIK3CA copy-number gain and inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast cancer.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2023 May 9;9(2):a006255. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a006255. Print 2023 Apr. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2023. PMID: 36863843 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast cancer: a review.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jun;169(3):397-406. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4697-y. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29417298 Review.
-
Impact of microRNA variants on PI3K/AKT signaling in triple-negative breast cancer: comprehensive review.Med Oncol. 2024 Aug 9;41(9):222. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02469-4. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39120634 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting PI3K signaling in Lung Cancer: advances, challenges and therapeutic opportunities.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 14;23(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06144-8. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39953539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Triple-Negative HCC1937 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Revealed the Regulation of Migration and Invasion via the Downregulation of the Genes JAK2, ROCK1 and ROCK2.ACS Omega. 2025 Jul 9;10(28):31187-31200. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c05895. eCollection 2025 Jul 22. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40727786 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Subtypes and Mechanisms of Breast Cancer: Precision Medicine Approaches for Targeted Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 25;17(7):1102. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071102. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular targets and therapies associated with poor prognosis of triple‑negative breast cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Jun;66(6):52. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5758. Epub 2025 May 30. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40444482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

