Jolkinolide B Ameliorates Liver Inflammation and Lipogenesis by Regulating JAK/STAT3 Pathway
- PMID: 39370730
- PMCID: PMC11535294
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.033
Jolkinolide B Ameliorates Liver Inflammation and Lipogenesis by Regulating JAK/STAT3 Pathway
Abstract
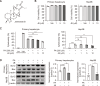
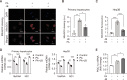
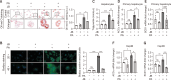
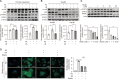
Hepatic dysregulation of lipid metabolism exacerbates inflammation and enhances the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). STAT3 has been linked to lipid metabolism and inflammation. Jolkinolide B (JB), derived from Euphorbia fischeriana, is known for its pharmacological anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. Therefore, this study investigated whether JB affects MASLD prevention by regulating STAT3 signaling. JB attenuated steatosis and inflammatory responses in palmitic acid (PA)-treated hepatocytes. Additionally, JB treatment reduced the mRNA expression of de-novo lipogenic genes, such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase and stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1. Interestingly, JB-mediated reduction in inflammation and lipogenesis was dependent on STAT3 signaling. JB consistently modulated mitochondrial dysfunction and the mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting PA-induced JAK/STAT3 activation. This study suggests that JB is a potential therapeutic agent to prevent major stages of MASLD through inhibition of JAK/STAT3 signaling in hepatocytes.
Keywords: Inflammation; Jolkinolide B; Lipid accumulation; MASLD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

