Follow Up Care After Penile Sparing Surgery for Penile Cancer: Current Perspectives
- PMID: 39371106
- PMCID: PMC11456267
- DOI: 10.2147/RRU.S465546
Follow Up Care After Penile Sparing Surgery for Penile Cancer: Current Perspectives
Abstract
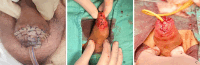
Penile cancer (PeCa) is a rare urologic tumor worldwide. In 2024, 2100 new cases and 500 deaths are estimated in the United States. Radical surgery via total penectomy has historically been the cornerstone of treatment, since it provides excellent long-term oncological control. The rationale of surgery for penile cancer was to achieve a 2 cm macroscopic surgical margin that is historically advocated to reduce recurrences. Over time, numerous studies have demonstrated that resection margin status does not affect patients' survival. Different penile-sparing techniques are currently recommended in the European Association of Urology-American Society of Clinical Oncology (EAU-ASCO) guidelines for the treatment of localized primary PeCa. Centralization of care could yield multiple benefits, including improved disease awareness, higher rates of penile-sparing surgery, enhanced detection rates, increased utilization of less invasive lymph node staging techniques, enhanced quality of specialized histopathological examinations, and the establishment of specialized multidisciplinary teams. Compared to more aggressive treatments, the higher recurrence rates after penile-sparing surgery do not hamper neither the metastasis-free survival nor the overall survival. Repeated penile-sparing surgery could be considered for selected cases. The psychological impact of penile cancer is not negligible since the perceived loss of masculinity might adversely affect mental health and overall well-being. Quality of life may be compromised by sexual and urinary dysfunction which may be the result either of the loss of penile tissue or the psychological status of the patient. It is of utmost importance to offer rehabilitative treatment as sexual therapy, physical therapy, occupational therapy, family and peer counseling.
Keywords: penile cancer; penile-sparing surgery; quality of life; sexual function; survival.
© 2024 Lasorsa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources