Coping and emotion regulation: A conceptual and measurement scoping review
- PMID: 39371329
- PMCID: PMC11449430
- DOI: 10.1037/cap0000377
Coping and emotion regulation: A conceptual and measurement scoping review
Abstract
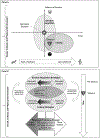
The fields of coping and emotion regulation have mostly evolved separately over decades, although considerable overlap exists. Despite increasing efforts to unite them from a conceptual standpoint, it remains unclear whether conceptual similarities translate into their measurement. The main objective of this review was to summarize and compare self-reported measures of coping and emotion regulation strategies. The secondary objective was to examine whether other psychological measures (e.g., resilience) indirectly reflect regulatory strategies' effectiveness, thus representing additionally informative approaches. Results indicated substantial overlap between coping and emotion regulation measures. In both frameworks, two to eight individual strategies were usually captured, but only a third included ≤20 items. Most commonly evaluated strategies were reappraisal/reinterpretation, active coping/problem-solving, acceptance, avoidance, and suppression. Evidence also suggested psychological distress and well-being measures, especially in certain contexts like natural stress experiments, and resilience measures are possible indirect assessments of these regulatory strategies' effectiveness. These results are interpreted in the light of a broader, integrative affect regulation framework and a conceptual model connecting coping, emotion regulation, resilience, psychological well-being and psychological distress is introduced. We further discussed the importance of alignment between individuals, contexts, and strategies used, and provide directions for future research. Altogether, coping and emotion regulation measures meaningfully overlap. Joint consideration of both frameworks in future research would widen the repertoire of available measures and orient their selection based on other aspects like length or strategies covered, rather than the framework only.
Keywords: coping; emotion regulation; measure; resilience; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Aldao A, Sheppes G, & Gross JJ (2015). Emotion regulation flexibility. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 39, 263–278. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s10608-014-9662-4 - DOI
-
- Arksey H, & O’Malley L (2005). Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology: Theory & Practice, 8(1), 19–32. https://doi.org/ 10.1080/1364557032000119616 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
