Precooked Jack Bean [ Canavalia ensiformis (L.) DC] Sprout: Generation of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides during Simulated Digestion
- PMID: 39371521
- PMCID: PMC11450285
- DOI: 10.3746/pnf.2024.29.3.345
Precooked Jack Bean [ Canavalia ensiformis (L.) DC] Sprout: Generation of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides during Simulated Digestion
Abstract
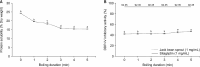
Bioactive peptides generated from jack bean sprouts are reported to function as dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors. However, no studies have investigated the effect of precooking followed by simulated digestion using pepsin-pancreatin to increase DPP-IV inhibitory peptide generation in jack bean sprouts. Therefore, the present study aimed to explore the generation of DPP-IV inhibitory peptides from precooked jack bean [Canavalia ensiformis (L.) DC] sprouts during simulated digestion with pepsin-pancreatin. The results showed that peptide fractions of the sample hydrolysate with molecular weight <1 kDa exhibited the strongest DPP-IV inhibitory activity (84.77%±0.49%) after simulated digestion. This activity was slightly greater than that (74.12%±0.85%) observed prior to simulated digestion. These findings demonstrate that the DPP-IV inhibitory activity of precooked jack bean sprouts can be retained following simulated digestion. Moreover, our investigation revealed the sequences of two novel peptides following simulated digestion with critical amino acids. The presence of alanine and glycine at the penultimate N-terminus of AAGPKP and LGDLLK confirmed the presence of DPP-IV inhibitors. Both peptide sequences are nontoxic and interact with the catalytic sites of enzymes through hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors; peptide fraction; peptide sequence; precooked jack bean sprout; simulated digestion.
© 2024 The Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHOR DISCLOSURE STATEMENT The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Agustia FC, Supriyadi S, Murdiati A, Indrati R. Germination of jack bean [Canavalia ensiformis (L.) DC.] and its impact on nutrient and anti-nutrient composition. Food Res. 2023b;7:210–218. doi: 10.26656/fr.2017.7(5).905. - DOI
-
- Bunsroem K, Prinyawiwatkul W, Thaiudom S. The influence of whey protein heating parameters on their susceptibility to digestive enzymes and the antidiabetic activity of hydrolysates. Foods. 2022;11:829. doi: 10.3390/foods11060829. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11060829. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
