Spiking representation learning for associative memories
- PMID: 39371606
- PMCID: PMC11450452
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1439414
Spiking representation learning for associative memories
Abstract
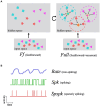
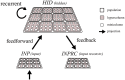
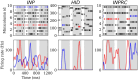
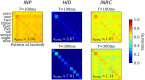
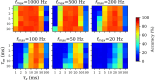
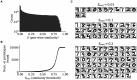
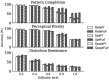
Networks of interconnected neurons communicating through spiking signals offer the bedrock of neural computations. Our brain's spiking neural networks have the computational capacity to achieve complex pattern recognition and cognitive functions effortlessly. However, solving real-world problems with artificial spiking neural networks (SNNs) has proved to be difficult for a variety of reasons. Crucially, scaling SNNs to large networks and processing large-scale real-world datasets have been challenging, especially when compared to their non-spiking deep learning counterparts. The critical operation that is needed of SNNs is the ability to learn distributed representations from data and use these representations for perceptual, cognitive and memory operations. In this work, we introduce a novel SNN that performs unsupervised representation learning and associative memory operations leveraging Hebbian synaptic and activity-dependent structural plasticity coupled with neuron-units modelled as Poisson spike generators with sparse firing (~1 Hz mean and ~100 Hz maximum firing rate). Crucially, the architecture of our model derives from the neocortical columnar organization and combines feedforward projections for learning hidden representations and recurrent projections for forming associative memories. We evaluated the model on properties relevant for attractor-based associative memories such as pattern completion, perceptual rivalry, distortion resistance, and prototype extraction.
Keywords: BCPNN; Hebbian learning; associative memory; attractor dynamics; representation learning; spiking neural networks; structural plasticity; unsupervised learning.
Copyright © 2024 Ravichandran, Lansner and Herman.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Amit D. J. (1989). Modeling brain function. The World of Attractor Neural Networks, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Anderson J. R., John R., Bower G. H., (1973). Human associative memory: A brief edition
-
- Bartlett F. C., Kintsch W., (1995). Remembering: A study in experimental and social psychology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

