Modulation of Inflammation in McCoy Cells by Zinc Nanoparticles Conjugated With β-Chitosan
- PMID: 39371713
- PMCID: PMC11456218
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.68653
Modulation of Inflammation in McCoy Cells by Zinc Nanoparticles Conjugated With β-Chitosan
Abstract
Introduction: This study investigated biosynthetically derived β-chitosan-derived zinc nanoparticles (β-Ch-Zn NPs) for their potential anti-inflammatory properties on McCoy cells. β-Ch-Zn NPs were synthesized using a green chemistry approach, and their characterization confirmed successful synthesis, appropriate size, and morphology. The study aimed to evaluate the cytotoxicity of β-Ch-Zn NPs and their effects on inflammatory responses in McCoy cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
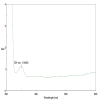
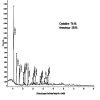
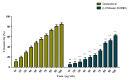
Methods: β-Ch-Zn NPs were synthesized and characterized using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction (XRD) to confirm their structural and morphological properties. The cytotoxicity of β-Ch-Zn NPs was assessed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay at various concentrations to determine safe doses for subsequent experiments. To induce inflammation, McCoy cells were pretreated with β-Ch-Zn NPs at different concentrations before LPS stimulations. Gene expression analysis using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to measure the messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of proinflammatory cytokine.
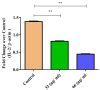
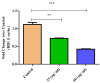
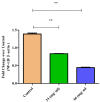
Results: FTIR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and XRD confirmed the successful synthesis of β-Ch-Zn NPs with the desired size and morphology. The MTT assay demonstrated concentration-dependent cytotoxicity of β-Ch-Zn NPs, indicating safety for cellular studies. Pretreatment with β-Ch-Zn NPs significantly downregulated the mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines. The nanoparticles effectively downregulate proinflammatory cytokines and promote anti-inflammatory pathways, as evidenced by the significant reduction in interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, hypoxia-inducible factor, and nuclear factor kappa B expression in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that biosynthetically derived β-Ch-Zn NPs exhibit potent anti-inflammatory effects in McCoy cells. These findings underscore the therapeutic potential of β-Ch-Zn NPs for treating inflammatory conditions and support further investigation into their in vivo efficacy and safety.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; cytokines; cytotoxicity; green synthesis; mccoy cells; β-chitosan nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2024, Payra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- An overview of inflammation: mechanism and consequences. Afsar A. Front Biol. 2011;6:274–281.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
