GPT-4o vs. Human Candidates: Performance Analysis in the Polish Final Dentistry Examination
- PMID: 39371744
- PMCID: PMC11456324
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.68813
GPT-4o vs. Human Candidates: Performance Analysis in the Polish Final Dentistry Examination
Abstract
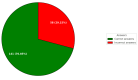
Background This study aims to evaluate the performance of OpenAI's GPT-4o in the Polish Final Dentistry Examination (LDEK) and compare it with human candidates' results. The LDEK is a standardized test essential for dental graduates in Poland to obtain their professional license. With artificial intelligence (AI) becoming increasingly integrated into medical and dental education, it is important to assess AI's capabilities in such high-stakes examinations. Materials and methods The study was conducted from August 1 to August 15, 2024, using the Spring 2023 LDEK exam. The exam comprised 200 multiple-choice questions, each with one correct answer among five options. Questions spanned various dental disciplines, including Conservative Dentistry with Endodontics, Pediatric Dentistry, Dental Surgery, Prosthetic Dentistry, Periodontology, Orthodontics, Emergency Medicine, Bioethics and Medical Law, Medical Certification, and Public Health. The exam organizers withdrew one question. GPT-4o was tested on these questions without access to the publicly available question bank. The AI model's responses were recorded, and each answer's confidence level was assessed. Correct answers were determined based on the official key provided by the Center for Medical Education (CEM) in Łódź, Poland. Statistical analyses, including Pearson's chi-square test and the Mann-Whitney U test, were performed to evaluate the accuracy and confidence of ChatGPT's answers across different dental fields. Results GPT-4o correctly answered 141 out of 199 valid questions (70.85%) and incorrectly answered 58 (29.15%). The AI performed better in fields like Conservative Dentistry with Endodontics (71.74%) and Prosthetic Dentistry (80%) but showed lower accuracy in Pediatric Dentistry (62.07%) and Orthodontics (52.63%). A statistically significant difference was observed between ChatGPT's performance on clinical case-based questions (36.36% accuracy) and other factual questions (72.87% accuracy), with a p-value of 0.025. Confidence levels also varied significantly between correct and incorrect answers, with a p-value of 0.0208. Conclusions GPT-4o's performance in the LDEK suggests it has potential as a supplementary educational tool in dentistry. However, the AI's limited clinical reasoning abilities, especially in complex scenarios, reveal a substantial gap between AI and human expertise. While ChatGPT demonstrates strong performance in factual recall, it cannot yet match the critical thinking and clinical judgment exhibited by human candidates.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; chatgpt; dentistry final medical examination; machine learning; medical education; medical professionals.
Copyright © 2024, Jaworski et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Artificial intelligence in medicine. Hamet P, Tremblay J. Metabolism. 2017;69S:0. - PubMed
-
- Can artificial intelligence predict COVID-19 mortality? Genc AC, Cekic D, Issever K, et al. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023;27:9866–9871. - PubMed
-
- A Chat(GPT) about the future of scientific publishing. Hill-Yardin EL, Hutchinson MR, Laycock R, Spencer SJ. Brain Behav Immun. 2023;110:152–154. - PubMed
-
- The rise of ChatGPT: Exploring its potential in medical education. Lee H. Anat Sci Educ. 2024;17:926–931. - PubMed
-
- Number of ChatGPT users. . https://explodingtopics.com/blog/chatgpt-users. Number of ChatGPT Users (Aug 2024) [ Aug; 2024 ]. 2024. https://explodingtopics.com/blog/chatgpt-users?utm_medium=email&utm_sour... https://explodingtopics.com/blog/chatgpt-users?utm_medium=email&utm_sour...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous