Advancing Albumin Isolation from Human Serum with Graphene Oxide and Derivatives: A Novel Approach for Clinical Applications
- PMID: 39371982
- PMCID: PMC11447712
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c04276
Advancing Albumin Isolation from Human Serum with Graphene Oxide and Derivatives: A Novel Approach for Clinical Applications
Abstract
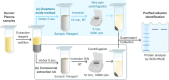
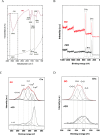
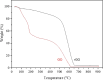
This study introduces a novel, environmentally friendly albumin isolation method using graphene oxide (GO). GO selectively extracts albumin from serum samples, leveraging the unique interactions between GO's oxygen-containing functional groups and serum proteins. This method achieves high purification efficiency without the need for hazardous chemicals. Comprehensive characterization of GO and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) through techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) confirmed the structural and functional group transformations crucial for protein binding. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and mass spectrometry analyses demonstrated over 95% purity of isolated albumin, with minimal contamination from other serum proteins. The developed method, optimized for pH and incubation conditions, showcases a green, cost-effective, and simple alternative for albumin purification, promising broad applicability in biomedical research and clinical applications.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures








References
-
- de Richter E. A.; Kiens B.; Galbo H.; Saltin B.. Skeletal Muscle Metabolism in Exercise and Diabetes (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology), 1st ed.; Springer, 1998; p 441.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
