Novel Bioproduction of 1,6-Hexamethylenediamine from l-Lysine Based on an Artificial One-Carbon Elongation Cycle
- PMID: 39372007
- PMCID: PMC11447709
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c06289
Novel Bioproduction of 1,6-Hexamethylenediamine from l-Lysine Based on an Artificial One-Carbon Elongation Cycle
Abstract
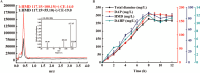
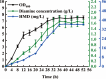
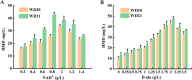
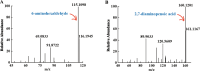
1,6-hexamethylenediamine (HMD) is an important precursor for nylon-66 material synthesis, while research on the bioproduction of HMD has been relatively scarce in scientific literature. As concerns about climate change, environmental pollution, and the depletion of fossil fuel reserves continue to grow, the significance of producing fundamental chemicals from renewable sources is becoming increasingly prominent. In recent investigations, the bioproduction of HMD from adipic acid has been reported but with lingering challenges concerning costly raw materials and low yields. Here, we have undertaken the reconstruction of the HMD synthetic pathway within Escherichia coli, which was constituted with l-lysine α-oxidase (Raip), LeuABCD, α-ketoacid decarboxylase (KivD), and transaminases (Vfl), leveraging a carbon chain extension module and a metabolic pathway of transaminase-decarboxylase cascade catalysis within the strain WD20, which successfully produce 46.7 ± 2.0 mg/L HMD. To increase the cascade activity and create a higher tolerance to external environmental disturbance for l-lysine to convert into HMD, another two enzymes d-alanine aminotransferase (Dat) and alpha-ketoacid decarboxylase (KdcA) were introduced into WD21 to provide flux flexibility for α-ketoacid metabolization, which was named "Smart-net metabolic engineering" in our research, and high-efficiency synthesis of HMD utilizing l-lysine as the substrate has been successfully achieved. Finally, we established a + 1C bioconversion multienzyme cascade catalyzing up to 65% conversion of l-lysine to HMD. Notably, our fermentation process yielded an impressive 213.5 ± 8.7 mg/L, representing the highest reported yield to date for the bioproduction of HMD from l-lysine.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
One-Pot Biocatalytic Transformation of Adipic Acid to 6-Aminocaproic Acid and 1,6-Hexamethylenediamine Using Carboxylic Acid Reductases and Transaminases.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Jan 15;142(2):1038-1048. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b11761. Epub 2020 Jan 7. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 31886667
-
De Novo Production of 1,6-Hexanediol and 1,6-Hexamethylenediamine from Glucose by Metabolic Engineered Escherichia coli.ACS Synth Biol. 2025 Feb 21;14(2):598-608. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00881. Epub 2025 Feb 12. ACS Synth Biol. 2025. PMID: 39936844
-
Metabolic engineering combined with site-directed saturated mutations of α-keto acid decarboxylase for efficient production of 6-aminocaproic acid and 1,6-hexamethylenediamine.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2024 Oct;121(10):3329-3337. doi: 10.1002/bit.28795. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 38956978
-
[Molecular engineering and immobilization of lysine decarboxylase for synthesis of 1, 5-diaminopentane: a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022 Dec 25;38(12):4403-4419. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.220400. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 36593185 Review. Chinese.
-
Enzymatic synthesis of chiral intermediates for Omapatrilat, an antihypertensive drug.Biomol Eng. 2001 Jun;17(6):167-82. doi: 10.1016/s1389-0344(01)00068-5. Biomol Eng. 2001. PMID: 11337276 Review.
References
-
- Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 1–8.
-
- Nopparut A.; Amornsakchai T. Influence of pineapple leaf fiber and it’s surface treatment on molecular orientation in, and mechanical properties of, injection molded nylon composites. Polym. Test. 2016, 52, 141–149. 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2016.04.012. - DOI
-
- Zhang C.; Cao M.; Jiang S.; Huang X.; Mai K.; Yan K. Quick analysis of composition of semi-aromatic copolyamide via 13C NMR study. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2019, 24 (1), 40–53. 10.1080/1023666X.2018.1514708. - DOI
-
- Fedorchuk T. P.; Khusnutdinova A. N.; Evdokimova E.; Flick R.; Di Leo R.; Stogios P.; Savchenko A.; Yakunin A. F. One-pot biocatalytic transformation of adipic acid to 6-aminocaproic acid and 1, 6-hexamethylenediamine using carboxylic acid reductases and transaminases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142 (2), 1038–1048. 10.1021/jacs.9b11761. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
