Successful Bevacizumab Therapy in a 25-Year-Old Patient with Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis
- PMID: 39372143
- PMCID: PMC11451837
- DOI: 10.12890/2024_004840
Successful Bevacizumab Therapy in a 25-Year-Old Patient with Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis
Abstract
Background: Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) is a chronic condition caused primarily by human papilloma virus (HPV) types 6 and 11, leading to recurrent growths in the respiratory tract. These types of papilloma can cause significant morbidity due to airway obstruction, often requiring frequent surgical interventions. Traditional treatments, including surgical removal and adjunctive therapies like antivirals and immune modulators, often fail to prevent recurrence, impacting the patient's quality of life.
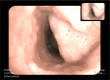
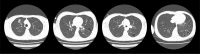
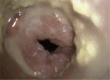
Case description: This report presents a 25-year-old female with a long-standing history of RRP, diagnosed at age 2. Despite numerous interventions, including CO2 laser ablations, interferon therapy, HPV vaccination, and a laryngotomy with tracheal reconstruction, the patient continued to experience severe airway obstruction requiring frequent surgeries. In 2023, intravenous therapy with bevacizumab, vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor was introduced, leading to a significant reduction in the frequency of surgical interventions from 8 to 4 per year. This reduction improved the patient's respiratory function and quality of life, highlighting bevacizumab's therapeutic potential.
Conclusion: The case underscores the debilitating nature of RRP and the challenges of its management. Bevacizumab, by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), has shown promise in reducing papilloma growth and the need for frequent surgeries. This case supports the inclusion of bevacizumab as an adjunctive therapy in RRP treatment, warranting further research to confirm its long-term efficacy and safety.
Learning points: Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is a rare and complex disease that severely impacts patients' quality of life.This case report demonstrates that bevacizumab can significantly reduce surgical interventions in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP), offering a promising treatment that improves management of this chronic condition.Bevacizumab, already used in treating various diseases by targeting VEGF, shows promise in managing RRP as well, highlighting its potential across multiple conditions and expanding its therapeutic versatility.
Keywords: Respiratory papillomatosis; VEGF; bevacizumab; bronchoscopy.
© EFIM 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: role of bevacizumab and HPV vaccination. A literature review with case presentations.Radiol Oncol. 2025 Feb 27;59(1):23-30. doi: 10.2478/raon-2025-0010. eCollection 2025 Mar 1. Radiol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40014785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bevacizumab chemotherapy for management of pulmonary and laryngotracheal papillomatosis in a child.Laryngoscope. 2017 Jul;127(7):1538-1542. doi: 10.1002/lary.26450. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Laryngoscope. 2017. PMID: 27996119
-
Rapid response to systemic bevacizumab therapy in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.Oncol Lett. 2014 Nov;8(5):1912-1918. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2486. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25289079 Free PMC article.
-
[Treatment of respiratory papillomatosis--a case report on systemic treatment with bevacizumab].Pneumologie. 2009 Jul;63(7):387-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1214714. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Pneumologie. 2009. PMID: 19591084 German.
-
Systemic bevacizumab as adjuvant therapy for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis in children: A series of three pediatric cases and literature review.Am J Otolaryngol. 2021 Sep-Oct;42(5):103126. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103126. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Am J Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 34175693 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources