Antioxidant properties of allium turcicum Özhatay & cowley plant extract, its effects on the proliferation and migration of cancer cells
- PMID: 39372216
- PMCID: PMC11449766
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1438634
Antioxidant properties of allium turcicum Özhatay & cowley plant extract, its effects on the proliferation and migration of cancer cells
Abstract
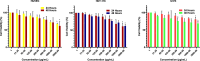
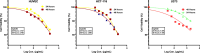
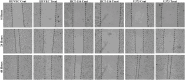
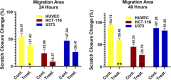
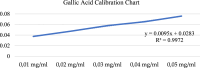
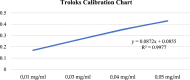
Cancer is a type of non-communicable disease that is responsible for numerous deaths worldwide. Cancer incidence and mortality rates are on the rise due to a combination of factors, such as a growing population, aging, and poor dietary habits. The Allium turcicum Özhatay & Cowley plant is an endemic plant in the area where it grows and is consumed by the public due to its various benefits. This endemic plant, which generally grows in high-altitude regions, is sold in bunches because it is costly, mixed with rock salt, crushed into powder, and consumed as a spice. The cytotoxic and growth-inhibitory effects of A. turcicum Özhatay & Cowley herb extract on human glioblastoma U373 cells, human colorectal carcinoma cell HCT-116, and healthy HUVEC cell lines were determined by the MTT method. After 24 and 48 h of application, logIC50 values in HUVEC, HCT-116, and U373 cells were defined as 3.737, 3.765; 3.513, 3.696, 4.476, and 4.104 μg/mL, respectively. We conducted a cell migration experiment to study the A. turcicum Özhatay & Cowley Extract (ATÖCE) impact on cancer cells' metastatic behavior. Our findings indicate that ATÖCE has an inhibitory effect on the migration potential of the cells used in the study. We conducted experiments using DPPH, ABTS, CUPRAC, and total phenolic content to assess the antioxidant properties of ATÖCE. The findings from the antioxidant activity experiments revealed an activity level of 0.20 ± 0.046 at IC50. Additionally, the total phenolic content was measured to be 0.26 ± 0.044 mg GAE/g.
Keywords: Allium turcicum Özhatay & Cowley; Cytotoxicity; cancer; cell viability; glioblastoma; migration.
Copyright © 2024 İPEK, Baran, Cebe, Ahmadian, Eftekhari and Baran.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdullah Thani N. A., Sallis B., Nuttall R., Schubert F. R., Ahsan M., Davies D., et al. (2012). Induction of apoptosis and reduction of MMP gene expression in the U373 cell line by polyphenolics in Aronia melanocarpa and by curcumin. Oncol. Rep. 28 (4), 1435–1442. 10.3892/or.2012.1941 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Afrin S., Giampieri F., Gasparrini M., Forbes-Hernández T. Y., Cianciosi D., Reboredo-Rodriguez P., et al. (2020). Dietary phytochemicals in colorectal cancer prevention and treatment: A focus on the molecular mechanisms involved. Biotechnol. Adv. 38, 107322. 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aslankoç R., Demirci D., Ümmahan İ., Yildiz M., Öztürk A., Çetin M., et al. (2019). The role of antioxidant enzymes in oxidative stress – superoxide dismutase(SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione pe-roxidase (GPx). SDU Med. Fac. J. 26 (3), 362–369. 10.17343/sdutfd.566969 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

