Lactate's impact on immune cells in sepsis: unraveling the complex interplay
- PMID: 39372401
- PMCID: PMC11449721
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483400
Lactate's impact on immune cells in sepsis: unraveling the complex interplay
Abstract
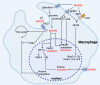
Lactate significantly impacts immune cell function in sepsis and septic shock, transcending its traditional view as just a metabolic byproduct. This review summarizes the role of lactate as a biomarker and its influence on immune cell dynamics, emphasizing its critical role in modulating immune responses during sepsis. Mechanistically, key lactate transporters like MCT1, MCT4, and the receptor GPR81 are crucial in mediating these effects. HIF-1α also plays a significant role in lactate-driven immune modulation. Additionally, lactate affects immune cell function through post-translational modifications such as lactylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation, which alter enzyme activities and protein functions. These interactions between lactate and immune cells are central to understanding sepsis-associated immune dysregulation, offering insights that can guide future research and improve therapeutic strategies to enhance patient outcomes.
Keywords: immune cells; immune response; immunosuppression; inflammation; lactate; lactic acid; lactylation; sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Chen, Kueth, Shao, Wang, Ha, Williams, Li, Fan and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

