Nodule-Specific NRF2-Targeted Upregulation in Patients With KEAP1 Mutations and Familial Nontoxic Multinodular Goiter
- PMID: 39373520
- PMCID: PMC11913113
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgae699
Nodule-Specific NRF2-Targeted Upregulation in Patients With KEAP1 Mutations and Familial Nontoxic Multinodular Goiter
Abstract
Context: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) is associated with nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (NRF2) and promotes NRF2 degradation in normal conditions. Genetic abnormality in KEAP1 is a rare disease and presents with familial multinodular goiter.
Objective: This study assessed the clinical and molecular findings concerning nodular formation in the thyroid gland of patients harboring KEAP1 germline mutations.
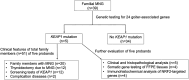
Methods: Next-generation sequencing analysis targeting goiter-associated genes was performed on 39 patients with familial multinodular goiter. The expression of NRF2-targeted genes from surgical thyroid specimens of patients with KEAP1 mutations were analyzed using a whole-transcript expression array and immunohistochemistry.
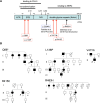
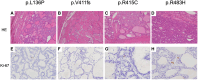
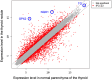
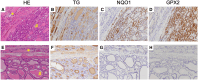
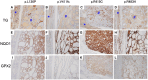
Results: We found 5 probands with pathogenic heterozygous mutations in KEAP1 (p.Q86*, p.L136P, p.V411fs, p.R415C, and p.R483H) that had no meaningful concomitance with mutations of other goiter-associated genes at germline and somatic levels. Their common histopathological features showed multinodular goiters in the entire thyroid gland with few degenerative lesions or complications of malignancy and slow proliferation indicating less than 1% at the Ki-67 labeling index. Among 42 NRF2-targeted genes, antioxidant genes were most frequently upregulated (11/12) in the nodule, followed by detoxification genes (6/11). Immunohistochemical analysis showed relatively high expression of glutathione peroxidase 2 and NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (representative NRF2-targeted genes) in the nodules of various patients harboring KEAP1 mutations.
Conclusion: KEAP1 germline heterozygous mutations exert excessive NRF2 activity in the thyroid gland and may confer cytoprotective effects even under abundant reactive oxygen species associated with thyroid hormone production, resulting in thyroid hyperplasia with scarce degradation.
Keywords: KEAP1 germline mutation; NRF2-targeted gene; familial goiter; multinodular goiter.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board . Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors. Vol. 8, 5th Ed. WHO; 2022. https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

