IMPACT OF REAL-LIFE ENVIRONMENTAL EXPOSURES ON REPRODUCTION: Rodent reproductive behavior among males and females after exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals
- PMID: 39374114
- PMCID: PMC11655000
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-24-0145
IMPACT OF REAL-LIFE ENVIRONMENTAL EXPOSURES ON REPRODUCTION: Rodent reproductive behavior among males and females after exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals
Abstract
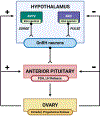
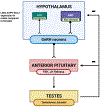
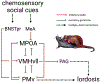
In brief: The rodent reproductive behavioral control column of the hypothalamus and the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis are critical systems that regulate copulatory behaviors in both males and females. We review how endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), specifically phthalates, bisphenol A, and chemical mixtures, dysregulate appetitive and consummatory copulatory behaviors and their neuroendocrine substrates, using mouse and rodent models.
Abstract: Sexual reproduction - from both physiological and behavioral perspectives - is dependent upon appropriate connections between a diverse, hormone-modulated network of neural regions. Importantly, these substrates are regulated by hormones across the lifespan from early development to adulthood, making them targets of EDCs. Rodents, such as mice and rats, are invaluable to the characterization of EDCs because of their sex-specific, stereotyped appetitive and consummatory reproductive behaviors. Phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), and EDC mixtures pose a salient risk to the health of humans, wildlife, and livestock because these synthetic compounds are ubiquitous due to their widespread use in the mass production of consumer and industrial goods. This review outlines how the HPG axis regulates male and female sexual behaviors, and how phthalates and BPA can perturb appetitive and consummatory behaviors and impact neural substrates that modulate reproductive behavior. We will then discuss how to progress toward a clearer understanding of the reproductive and neurobiological changes that occur due to EDC exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
IMPACT OF REAL-LIFE ENVIRONMENTAL EXPOSURES ON REPRODUCTION: Phthalate exposure and reproductive effects in rodents: a model for approaches on the protective role of natural products.Reproduction. 2025 Jan 2;169(1):e240186. doi: 10.1530/REP-24-0186. Print 2025 Jan 1. Reproduction. 2025. PMID: 39499862 Review.
-
IMPACT OF REAL-LIFE ENVIRONMENTAL EXPOSURES ON REPRODUCTION: Phthalates disrupt female reproductive health: a call for enhanced investigation into mixtures.Reproduction. 2025 Jan 9;169(2):e240117. doi: 10.1530/REP-24-0117. Print 2025 Feb 1. Reproduction. 2025. PMID: 39555988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, Hypothalamic Inflammation and Reproductive Outcomes: A Review of the Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 22;25(21):11344. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111344. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Executive Summary to EDC-2: The Endocrine Society's Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals.Endocr Rev. 2015 Dec;36(6):593-602. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1093. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Endocr Rev. 2015. PMID: 26414233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intersection of neurotoxicology and endocrine disruption.Neurotoxicology. 2012 Dec;33(6):1410-1419. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.05.014. Epub 2012 May 31. Neurotoxicology. 2012. PMID: 22659293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adam N, Brusamonti L, & Mhaouty-Kodja S (2021). Exposure of Adult Female Mice to Low Doses of di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate Alone or in an Environmental Phthalate Mixture: Evaluation of Reproductive Behavior and Underlying Neural Mechanisms. Environmental Health Perspectives, 129(1), 017008. 10.1289/EHP7662 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adewale HB, Jefferson WN, Newbold RR, & Patisaul HB (2009). Neonatal Bisphenol-A Exposure Alters Rat Reproductive Development and Ovarian Morphology Without Impairing Activation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Neurons1. Biology of Reproduction, 81(4), 690–699. 10.1095/biolreprod.109.078261 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

