The perivascular space is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid flow in humans: A proof-of-principle report
- PMID: 39374384
- PMCID: PMC11494350
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2407246121
The perivascular space is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid flow in humans: A proof-of-principle report
Abstract
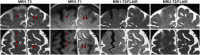
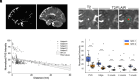
The glymphatic pathway was defined in rodents as a network of perivascular spaces (PVSs) that facilitates organized distribution of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into the brain parenchyma. To date, perivascular CSF and cerebral interstitial fluid exchange has not been shown in humans. Using intrathecal gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI, we show that contrast-enhanced CSF moves through the PVS into the parenchyma, supporting the existence of a glymphatic pathway in humans.
Keywords: MRI; cerebrospinal fluid; glymphatic; perivascular space.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rennels M. L., Gregory T. F., Blaumanis O. R., Fujimoto K., Grady P. A., Evidence for a ‘Paravascular’ fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain from the subarachnoid space. Brain Res. 326, 47–63 (1985). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

