Digital cognitive behavioral therapy vs education for pain in adults with sickle cell disease
- PMID: 39374587
- PMCID: PMC11699089
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024013861
Digital cognitive behavioral therapy vs education for pain in adults with sickle cell disease
Abstract
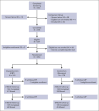
Despite the burden of chronic pain in sickle cell disease (SCD), nonpharmacological approaches remain limited. This multisite, randomized trial compared digital cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) with a digital pain/SCD education program ("Education") for managing pain and related symptoms. Participants were recruited virtually from seven SCD centers and community organizations in the United States. Adults (aged ≥18 years) with SCD-related chronic pain and/or daily opioid use were assigned to receive either CBT or Education for 12 weeks. Both groups used an app with interactive chatbot lessons and received personalized health coach support. The primary outcome was the change in pain interference at six months, with secondary outcomes including pain intensity, depression, anxiety, quality of life, and self-efficacy. Of 453 screened participants, 359 (79%) were randomized to CBT (n = 181) or Education (n = 178); 92% were Black African American, and 66.3% were female. At six months, 250 participants (70%) completed follow-up assessments, with 16 (4%) withdrawals. Engagement with the chatbot varied, with 76% connecting and 48% completing at least one lesson, but 80% of participants completed at least one health coach session. Both groups showed significant within-group improvements in pain interference (CBT: -2.13; Education: -2.66), but no significant difference was observed between them (mean difference, 0.54; P = .57). There were no between-group differences in pain intensity, depression, anxiety, or quality of life. High engagement with health coaching and variable engagement with digital components may explain the similar outcomes between interventions in this diverse, hard-to-reach population.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hassell KL. Population estimates of sickle cell disease in the U.S. Am J Prev Med. Apr 2010;38(4):S512–S521. - PubMed
-
- Yawn BP, Buchanan GR, Afenyi-Annan AN, et al. Management of sickle cell disease: summary of the 2014 evidence-based report by expert panel members. JAMA. 2014;312(10):1033–1048. - PubMed
-
- Ballas SK, Gupta K, Adams-Graves P. Sickle cell pain: a critical reappraisal. Blood. 2012;120(18):3647–3656. - PubMed
-
- Smith WR, Penberthy LT, Bovbjerg VE, et al. Daily assessment of pain in adults with sickle cell disease. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148(2):94–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

