Structural basis for receptor-binding domain mobility of the spike in SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 and JN.1
- PMID: 39375326
- PMCID: PMC11458767
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52808-2
Structural basis for receptor-binding domain mobility of the spike in SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 and JN.1
Abstract
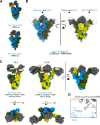
Since 2019, SARS-CoV-2 has undergone mutations, resulting in pandemic and epidemic waves. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, crucial for cellular entry, binds to the ACE2 receptor exclusively when its receptor-binding domain (RBD) adopts the up-conformation. However, whether ACE2 also interacts with the RBD in the down-conformation to facilitate the conformational shift to RBD-up remains unclear. Herein, we present the structures of the BA.2.86 and the JN.1 spike proteins bound to ACE2. Notably, we successfully observed the ACE2-bound down-RBD, indicating an intermediate structure before the RBD-up conformation. The wider and mobile angle of RBDs in the up-state provides space for ACE2 to interact with the down-RBD, facilitating the transition to the RBD-up state. The K356T, but not N354-linked glycan, contributes to both of infectivity and neutralizing-antibody evasion in BA.2.86. These structural insights the spike-protein dynamics would help understand the mechanisms underlying SARS-CoV-2 infection and its neutralization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- WHO. BA.2.86 Initial Risk Evaluation, 21 November, 2023.) (2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- JP223fa627009/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JP24jf0126002/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JP20ae0101047/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JPJSCCA20240006/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JPMJCR20H8/MEXT | JST | Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

