COVID-19 mRNA booster vaccination induces robust antibody responses but few adverse events among SARS-CoV-2 naïve nursing home residents
- PMID: 39375365
- PMCID: PMC11458568
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73004-8
COVID-19 mRNA booster vaccination induces robust antibody responses but few adverse events among SARS-CoV-2 naïve nursing home residents
Abstract
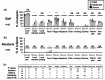
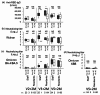
Residents in nursing homes face heightened COVID-19 risks. We aimed to assess the adverse events (AEs) rates and antibody responses after the first to the fifth dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in a nursing home cohort. Ninety-five SARS-CoV-2 naïve participants consisted of 26 staff (median age, 51 years) and 69 residents (median age, 88 years). Life-threatening AEs were reported in neither residents nor staff. The severity of non-life-threatening AEs was graded, and severe AEs were reported only in staff. The AEs rates were considerably lower in residents, compared to those in staff. Anti-RBD IgG and the neutralizing titers (NTs) against Wuhan and Omicron BA.4/BA.5 did not differ significantly between those with 'any AE' and 'no AE' among both staff and residents two months after the second, third and fifth doses, while the anti-RBD IgG significantly differed between two groups after third dose in residents. These findings suggest that the anti-RBD IgG and the NTs increase regardless of the occurrence of AEs. Our study underscores a robust antibody response in both in staff and residents, and fewer AEs following COVID-19 vaccination in SARS-CoV-2 naïve residents than staff, supporting the recommendation for mRNA booster doses in older adults at high-risk care facilities.
Keywords: COVID-19; Life-threatening adverse events; MRNA booster vaccination; Nursing home residents; Omicron variants; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Tamura, K. et al. Impact of COVID-19 and closed transmission of SARS-CoV-2 during the first wave in Toyama Prefecture, Japan, March 30 to May 18, 2020. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis.77, 75–82 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Comas-Herrera, A. et al. LT Covid International Living Report on COVID-19 and Long-Term Care (2022). https://ltccovid.org/international-living-report-covid-ltc/
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

