Residual disease is the main, but not the only factor impacting satisfaction in psoriatic patients undergoing biological therapies
- PMID: 39375798
- PMCID: PMC11840224
- DOI: 10.1111/ijd.17509
Residual disease is the main, but not the only factor impacting satisfaction in psoriatic patients undergoing biological therapies
Abstract
Background: Despite advancements in psoriasis treatment, a gap remains in aligning patient satisfaction with clinical outcomes. Our study aimed to evaluate which clinical and psychological factors may impact treatment satisfaction in psoriatic patients undergoing long-term biological therapies.
Methods: We performed an observational, cross-sectional, single-center study involving adult patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis treated with biologics for at least 12 months. We collected sociodemographic characteristics and data on the course of the psoriasis. We also assessed the absolute (residual) Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI), the site of the residual disease, and the severity of pruritus through the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). Satisfaction was evaluated using the Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQMv.II). The Type D Personality Scale (DS14 questionnaire and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 assessed the psychological profile.
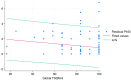
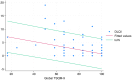
Results: Overall, 146 patients were included, and 82.1% were globally satisfied (global satisfaction TSQM score >75). Linear regression analysis showed a negative correlation between global satisfaction scoring and residual PASI. The multivariable analysis found a higher VAS-pruritus score (OR = 1.20, 95% CI = 1.01-1.44; P = 0.043) and not reaching a residual PASI < 2 (OR = 0.30, 95% CI = 0.09-0.94, P = 0.039) as the strongest predictors of global unsatisfied patients (TSQM < 75%). Other factors unrelated to residual disease, such as gender, class of biologic agent, and type D personality, have also been found to impact patient satisfaction.
Conclusions: Our study's findings underscore the complexity of patient satisfaction in psoriasis management and highlight the multifactorial nature of treatment success beyond traditional clinical measures.
Keywords: biologics; inflammatory diseases; psoriasis; quality of life; satisfaction; therapies.
© 2024 The Author(s). International Journal of Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the International Society of Dermatology.
Figures
References
-
- Kolli SS, Amin SD, Pona A, Cline A, Feldman SR. Psychosocial impact of psoriasis: a review for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2018;102(5S):21–25. - PubMed
-
- Manalo IF, Gilbert KE, Wu JJ. Time to raise the bar to psoriasis area severity index 90 and 100. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:1086–1088. - PubMed
-
- Reich K, Papp KA, Blauvelt A, Langley RG, Armstrong A, Warren RB, et al. Bimekizumab versus ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (BE VIVID): efficacy and safety from a 52‐week, multicentre, double‐blind, active comparator and placebo controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397(10273):487–498. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00125-2. Erratum in: Lancet. 2021;397(10275):670. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous