LEAP! Rx: A randomized trial of a pragmatic approach to lifestyle medicine
- PMID: 39376152
- PMCID: PMC11667554
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14265
LEAP! Rx: A randomized trial of a pragmatic approach to lifestyle medicine
Abstract
Introduction: Clinicians lack the tools to incorporate physical activity into clinical care for Alzheimer's disease prevention. We tested a 52-week exercise and health education program (Lifestyle Empowerment for Alzheimer's Prevention [LEAP! Rx]) that integrates clinician referrals and community-based fitness resources.
Methods: We randomized 219 participants to the LEAP! Rx (ie, exercise and monthly brain health education) or a standard-of-care control group and tested the effects on cardiorespiratory fitness, insulin resistance, body composition, lipids, and cognitive performance.
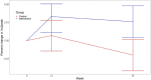
Results: Physicians were able to connect their patients to a community lifestyle intervention. The intervention group increased in cardiorespiratory fitness at 12 and 52 weeks (p = 0.005). We observed no effects on secondary measures. Participants meeting 80% of weekly goals (150 min, moderate to vigorous activity) saw greater fitness improvements than those with less than 80% (p < 0.001).
Discussion: These results hold promise for broad implementation of exercise interventions into larger healthcare systems and have implications for improved research recruitment strategies.
Trial registration: NCT No. NCT03253341.
Highlights: Our community-based exercise program increased cardiorespiratory fitness. Our digital physician referral method increased the diversity of the participant sample. Our findings have implications for personalized dementia risk reduction strategies.
Keywords: cardiorespiratory fitness; exercise; exercise prescription; health care delivery; healthy lifestyle; intervention; physical activity; randomized controlled trial (RCT); recruitment.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures
References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services . 2020 Profile of Older Americans. 2021.
-
- Nelson ME, et al. Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2007;116(9):1094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical