Ewing's Sarcoma of Maxillary Sinus
- PMID: 39376421
- PMCID: PMC11456048
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-024-04834-1
Ewing's Sarcoma of Maxillary Sinus
Abstract
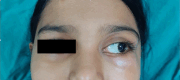
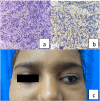
Ewing's sarcoma is a small round cell tumor commonly involving long bones. Head and neck involvement is seen less frequently with maxillary sinus being the rarest site. Here we report a case of a12-year-old female patient presented with left side facial swelling for 3 weeks duration which was diffuse and hard on palpation. CT and MRI of Nose & para nasal sinus revealed a mass lesion in the left maxillary sinus infiltrating and eroding the orbital wall and extending intracranially. Biopsy from the lesion revealed Ewing's sarcoma with strong positivity for CD-99 marker. Patient was referred to radiotherapy due to extensive disease at younger age. The CT and MRI along with HPE and IHC markers enables early diagnosis and prompt treatment that leads to better survival and prognosis, as unlike Ewing's sarcoma of long bones, that metastasize early. The combined chemoradiotherapy is now the standard line of treatment along with close follow up for at least 2 years.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Ewing’s sarcoma; Maxilla; Paranasal sinus; Radiotherapy.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare “No conflict of interest”.
Figures

References
-
- Aurias A, Rimbaut C, Buffe D, Dubousset J, Mazabraud A (1983) Chromosomal translocations in Ewing’s sarcoma. N Engl J Med 309:496–497 - PubMed
-
- Jayakumar S, Power D (2005) Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET: a histopathological review. Int J Orthoped Surg 3:1–4
-
- Li M, Hoschar AP, Budd GT, Chao ST, Scharpf J (2013) Primary Ewing’s sarcoma of the ethmoid sinus with intracranial and orbital extension: case report and literature review. Am J Otolaryngol 34:563–568 - PubMed
-
- Cotterill SJ, Ahrens S, Paulussen M, Jurgens HF, Voute PA, Gadner H, Craft AW (2000) Prognostic factors in Ewing’s tumor of bone: analysis of 975 patients from the European intergroup cooperative Ewing’s sarcoma study group. J Clin Oncol 18:3108–3114 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
