Peptide-guided adaptor-CAR T-Cell therapy for the treatment of SSTR2-expressing neuroendocrine tumors
- PMID: 39376579
- PMCID: PMC11457607
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2024.2412371
Peptide-guided adaptor-CAR T-Cell therapy for the treatment of SSTR2-expressing neuroendocrine tumors
Abstract
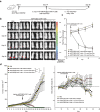
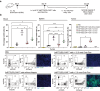
Somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2) is one of the five subtypes of somatostatin receptors and is overexpressed on the surface of most gastro-entero-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs), pituitary tumors, paraganglioma, and meningioma, as well as hepatocellular carcinoma and breast cancer. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells are genetically engineered to express an artificial, T-cell activating binder, leading upon ligation to biocidal activity against target-antigen expressing cells. Adaptor-CAR T-cells recognize, via the CAR, a tag on an antigen-binding molecule, building an activating bridge between the CAR and the target cell. We hypothesized that a novel fluorescent-peptide antagonist of SSTR2, called Octo-Fluo, in combination with anti-FITC adaptor CAR (AdFITC(E2)-CAR) T-cells, may function as an on-off tunable activating bridge between the CAR and SSTR2 expressing target cells. In vitro studies confirmed the binding of Octo-Fluo to Bon1-SSTR2 mCherry-Luc cells without evidence of internalization. AdFITC(E2)-CAR T-cells were activated and efficiently induced Bon1-SSTR2 cell death in vitro, in an Octo-Fluo concentration-dependent manner. Similarly, AdFITC(E2)-CAR T-cells in combination with Octo-Fluo efficiently infiltrated the tumor and eliminated Bon1-SSTR2 tumors in immunodeficient mice in therapeutic settings. Both, AdFITC(E2)-CAR T-cell tumor infiltration and biocidal activity were Octo-Fluo concentration-dependent, with high doses of Octo-Fluo, saturating both the CAR and the SSTR2 antigen independently, leading to the loss of tumor infiltration and biocidal activity due to the loss of bridge formation. Our findings demonstrate the potential of using AdFITC(E2)-CAR T-cells with Octo-Fluo as a versatile, on-off tunable bispecific adaptor for targeted CAR T-cell immunotherapy against SSTR2-positive NETs.
Keywords: Adaptor-CAR T-cell; Octo-fluo bispecific adaptor; SSTR2; neuroendocrine tumors.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CP, GB, NF, DN, FB and MGM are inventors of a patent application that describes the Octo-Fluo molecule.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
