Cooperation objective evaluation in aviation: validation and comparison of two novel approaches in simulated environment
- PMID: 39376698
- PMCID: PMC11457730
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2024.1409322
Cooperation objective evaluation in aviation: validation and comparison of two novel approaches in simulated environment
Abstract
Introduction: In operational environments, human interaction and cooperation between individuals are critical to efficiency and safety. These states are influenced by individuals' cognitive and emotional states. Human factor research aims to objectively quantify these states to prevent human error and maintain constant performances, particularly in high-risk settings such as aviation, where human error and performance account for a significant portion of accidents.
Methods: Thus, this study aimed to evaluate and validate two novel methods for assessing the degree of cooperation among professional pilots engaged in real-flight simulation tasks. In addition, the study aimed to assess the ability of the proposed metrics to differentiate between the expertise levels of operating crews based on their levels of cooperation. Eight crews were involved in the experiments, consisting of four crews of Unexperienced pilots and four crews of Experienced pilots. An expert trainer, simulating air traffic management communication on one side and acting as a subject matter expert on the other, provided external evaluations of the pilots' mental states during the simulation. The two novel approaches introduced in this study were formulated based on circular correlation and mutual information techniques.
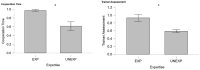
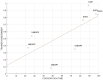
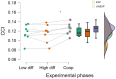
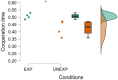
Results and discussion: The findings demonstrated the possibility of quantifying cooperation levels among pilots during realistic flight simulations. In addition, cooperation time is found to be significantly higher (p < 0.05) among Experienced pilots compared to Unexperienced ones. Furthermore, these preliminary results exhibited significant correlations (p < 0.05) with subjective and behavioral measures collected every 30 s during the task, confirming their reliability.
Keywords: approach-withdrawal; circular correlation; cooperation; electroencephalography; human factors; mental workload; mutual information; neurophysiological.
Copyright © 2024 Capotorto, Ronca, Sciaraffa, Borghini, Di Flumeri, Mezzadri, Vozzi, Giorgi, Germano, Babiloni and Aricò.
Conflict of interest statement
VR, NS, GB, GD, AV, AG, FB, and PA were employed by BrainSigns srl. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




References
-
- Berens P. (2009). CircStat: a MATLAB toolbox for circular statistics. J. Stat. Softw. 31, 1–21. 10.18637/jss.v031.i10 - DOI
-
- Bevilacqua D., Davidesco I., Wan L., Chaloner K., Rowland J., Ding M., et al. (2019). Brain-to-brain synchrony and learning outcomes vary by student-teacher dynamics: evidence from a real-world classroom electroencephalography study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 31, 401–411. 10.1162/jocn_a_01274 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borghini G., Aricó P., Di Flumeri G., Colosimo A., Storti S. F., Menegaz G., et al. (2016). “Neurophysiological measures for users' training objective assessment during simulated robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery,” in Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 981–984. 10.1109/EMBC.2016.7590866 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

