Computing optimal drug dosing regarding efficacy and safety: the enhanced OptiDose method in NONMEM
- PMID: 39377900
- PMCID: PMC11579100
- DOI: 10.1007/s10928-024-09940-9
Computing optimal drug dosing regarding efficacy and safety: the enhanced OptiDose method in NONMEM
Abstract
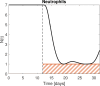
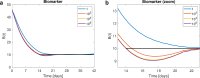
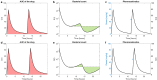
Recently, an optimal dosing algorithm (OptiDose) was developed to compute the optimal drug doses for any pharmacometrics model for a given dosing scenario. In the present work, we enhance the OptiDose concept to compute optimal drug dosing with respect to both efficacy and safety targets. Usually, these are not of equal importance, but one is a top priority, that needs to be satisfied, whereas the other is a secondary target and should be achieved as good as possible without failing the top priority target. Mathematically, this leads to state-constrained optimal control problems. In this paper, we elaborate how to set up such problems and transform them into classical unconstrained optimal control problems which can be solved in NONMEM. Three different optimal dosing tasks illustrate the impact of the proposed enhanced OptiDose method.
Keywords: Dose optimization; Efficacy; Optimal control; Optimal dosing; Safety; State constraints.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Bachmann F, Koch G, Pfister M, Szinnai G, Schropp J (2023) OptiDose: computing optimal drug dosing with OptiDose: implementation in NONMEM. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 50(3):173–188 - PubMed
-
- Beal SL, Sheiner LB, Boeckmann AJ, Bauer RJ (eds) NONMEM 7.5.1 users guides (1989-2024). ICON plc, Gaithersburg. https://nonmem.iconplc.com/nonmem751
-
- Koch G, Walz A, Lahu G, Schropp J (2009) Modeling of tumor growth and anticancer of combination therapy. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 36(2):179–197 - PubMed
-
- Friberg LE, Henningsson A, Mass H, Nguyen L, Karlsson MO (2002) Model of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression with parameter consistency across drugs. J Clin Oncol 20(24):4713–4721 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

