Unmasking biases and navigating pitfalls in the ophthalmic artificial intelligence lifecycle: A narrative review
- PMID: 39378192
- PMCID: PMC11460710
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000618
Unmasking biases and navigating pitfalls in the ophthalmic artificial intelligence lifecycle: A narrative review
Abstract
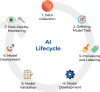
Over the past 2 decades, exponential growth in data availability, computational power, and newly available modeling techniques has led to an expansion in interest, investment, and research in Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications. Ophthalmology is one of many fields that seek to benefit from AI given the advent of telemedicine screening programs and the use of ancillary imaging. However, before AI can be widely deployed, further work must be done to avoid the pitfalls within the AI lifecycle. This review article breaks down the AI lifecycle into seven steps-data collection; defining the model task; data preprocessing and labeling; model development; model evaluation and validation; deployment; and finally, post-deployment evaluation, monitoring, and system recalibration-and delves into the risks for harm at each step and strategies for mitigating them.
Copyright: © 2024 Nakayama et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
LAC is the Editor-In-Chief of PLOS Digital Health.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang D, Maslej N, Brynjolfsson E, Etchemendy J, Lyons T, Manyika J, et al.. The AI Index 2022 Annual Report. In: aiindex.stanford.edu [Internet]. [cited 2022 Dec 16]. Available from: https://aiindex.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/2022-AI-Index-Re....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous