Antiviral Susceptibility of Swine-Origin Influenza A Viruses Isolated from Humans, United States
- PMID: 39378870
- PMCID: PMC11521183
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3011.240892
Antiviral Susceptibility of Swine-Origin Influenza A Viruses Isolated from Humans, United States
Abstract
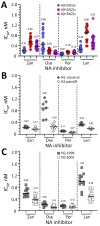
Since 2013, a total of 167 human infections with swine-origin (variant) influenza A viruses of A(H1N1)v, A(H1N2)v, and A(H3N2)v subtypes have been reported in the United States. Analysis of 147 genome sequences revealed that nearly all had S31N substitution, an M2 channel blocker-resistance marker, whereas neuraminidase inhibitor-resistance markers were not found. Two viruses had a polymerase acidic substitution (I38M or E199G) associated with decreased susceptibility to baloxavir, an inhibitor of viral cap-dependent endonuclease (CEN). Using phenotypic assays, we established subtype-specific susceptibility baselines for neuraminidase and CEN inhibitors. When compared with either baseline or CEN-sequence-matched controls, only the I38M substitution decreased baloxavir susceptibility, by 27-fold. Human monoclonal antibodies FI6v3 and CR9114 targeting the hemagglutinin's stem showed variable (0.03 to >10 µg/mL) neutralizing activity toward variant viruses, even within the same clade. Methodology and interpretation of laboratory data described in this study provide information for risk assessment and decision-making on therapeutic control measures.
Keywords: IRINA; United States; antimicrobial resistance; antivirals; baloxavir marboxil; hemagglutinin; human infections; influenza; monoclonal antibodies; pandemic risk assessment; swine-origin influenza A virus; viruses.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

