Cytokine profiles and their correlation with clinical and blood parameters in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 39379404
- PMCID: PMC11461704
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-72564-z
Cytokine profiles and their correlation with clinical and blood parameters in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
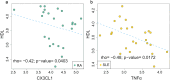
The abnormal biological activity of cytokines and their imbalance are implicated in developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Cytokine levels were measured in RA and SLE patients and compared to healthy controls using the Wilcoxon rank sum test and Kruskal-Wallis test. The relationship between cytokine levels and blood and clinical parameters was assessed using Spearman's correlation test. Compared to healthy controls, both RA and SLE patients exhibited elevated levels of GM-CSF, CX3CL1, IFN-α2, IL-12p70, IL-17A, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IFN-γ, which is evidence of their shared inflammatory signature. IL-2 levels were elevated exclusively in RA patients, while MCP-1 and IL-10 were uniquely increased in SLE patients. Notably, TNF-α showed the most significant increase in SLE patients. IL-4 was elevated in SLE patients with nephritis, correlating with IL-6, IL-10, sCD40L, and IL-8, suggesting B cell involvement in lupus nephritis. The negative correlation between CX3CL1 and TNF-α with HDL in RA and SLE respectively, highlights the potential association of these inflammatory markers with cardiovascular risk. These findings underscore the complex cytokine interplay in RA and SLE. CX3CL1 emerges as a potential therapeutic target for RA, while TNF-α and IL-4 show promise as therapeutic targets for SLE.
Keywords: Cytokines; Rheumatoid arthritis; Spearman’s correlation; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad, R. & Ahsan, H. Dual autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis with systemic lupus erythematosus and type 1 diabetes mellitus with multiple sclerosis. Rheumatol. Autoimmun.2, 120–128. 10.1002/rai2.12037 (2022).
-
- Smolen, J. S. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers.4, 1–23. 10.1038/nrdp.2018.1 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Fernández-Ávila, D. G., Rincón-Riaño, D. N., Bernal-Macías, S., Dávila, J. M. & Rosselli, D. Prevalencia de la artritis reumatoide en Colombia según información del Sistema Integral de Información de la Protección Social. Rev. Colombiana de Reumatol.26(2), 83–87. 10.1016/j.rcreu.2019.01.003 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Fernández-Ávila, D. G., Bernal-Macías, S., Rincón-Riaño, D. N., Gutiérrez Dávila, J. M. & Rosselli, D. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in Colombia: data from the national health registry 2012–2016. Lupus28, 1273–1278. 10.1177/0961203319864168 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

