Pharmacogenomics-assisted treatment versus standard of care in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39379847
- PMCID: PMC11463053
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-024-06104-4
Pharmacogenomics-assisted treatment versus standard of care in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Pharmacogenomic (PGx) factors significantly influence how patients respond to antipsychotic medications This systematic review was performed to synthesize the clinical utility of PGx-assisted treatment versus standard of care in schizophrenia.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane CENTRAL databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) from inception till June 2024 that had compared the clinical utility of PGx-assisted intervention as compared to the standard of care in schizophrenia. The primary outcome was safety, and the secondary outcomes were efficacy and medication adherence. Pooled standardized mean differences (SMD) along with a 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated (random-effects model) wherever feasible.
Results: A total of 18,821 studies were screened, and five were included for review. All the RCTs had a high risk of bias. Four studies included the commonly used antipsychotics. Three studies reported negative outcomes (safety, efficacy, and medication adherence) and two reported positive outcomes (safety) using different scales. In the meta-analysis, there were significant differences in the total Udvalg for Kliniske Undersogelser Side-Effect Rating scale score [SMD 0.95 (95% CI: 0.76-1.13), p < 0.001); I2 = 0%] and the total Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale score [SMD 10.65 (95% CI: 2.37-18.93), p = 0.01); I2 = 100%] between the PGx-assisted treatment and standard of care arms. However, the results were inconsistent, and the certainty of evidence (GRADE criteria) was very low.
Conclusion: Current evidence on the clinical utility of PGx-assisted treatment in schizophrenia is limited and inconsistent and further evidence is required in this regard.
Keywords: Antipsychotic; Pharmacogenomics (PGx); Precision medicine; Schizophrenia; Therapeutic drug monitoring.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
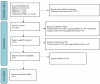

References
-
- Leucht S, Leucht C, Huhn M, Chaimani A, Mavridis D, Helfer B, Samara M, Rabaioli M, Bächer S, Cipriani A, Geddes JR, Salanti G, Davis JM. Sixty years of Placebo-controlled antipsychotic drug trials in Acute Schizophrenia: systematic review, bayesian Meta-analysis, and Meta-regression of efficacy predictors. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174(10):927–42. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, Keefe RS, Davis SM, Davis CE, Lebowitz BD, Severe J, Hsiao JK. Clinical antipsychotic trials of intervention effectiveness (CATIE) investigators. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(12):1209–23. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

