Nanobiotechnology boosts ferroptosis: opportunities and challenges
- PMID: 39379969
- PMCID: PMC11460037
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02842-5
Nanobiotechnology boosts ferroptosis: opportunities and challenges
Abstract
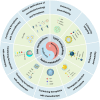
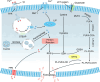
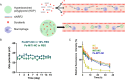
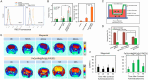
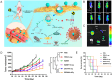
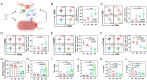
Ferroptosis, distinct from apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy, is a unique type of cell death driven by iron-dependent phospholipid peroxidation. Since ferroptosis was defined in 2012, it has received widespread attention from researchers worldwide. From a biochemical perspective, the regulation of ferroptosis is strongly associated with cellular metabolism, primarily including iron metabolism, lipid metabolism, and redox metabolism. The distinctive regulatory mechanism of ferroptosis holds great potential for overcoming drug resistance-a major challenge in treating cancer. The considerable role of nanobiotechnology in disease treatment has been widely reported, but further and more systematic discussion on how nanobiotechnology enhances the therapeutic efficacy on ferroptosis-associated diseases still needs to be improved. Moreover, while the exciting therapeutic potential of ferroptosis in cancer has been relatively well summarized, its applications in other diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, and kidney disease, remain underreported. Consequently, it is necessary to fill these gaps to further complete the applications of nanobiotechnology in ferroptosis. In this review, we provide an extensive introduction to the background of ferroptosis and elaborate its regulatory network. Subsequently, we discuss the various advantages of combining nanobiotechnology with ferroptosis to enhance therapeutic efficacy and reduce the side effects of ferroptosis-associated diseases. Finally, we analyze and discuss the feasibility of nanobiotechnology and ferroptosis in improving clinical treatment outcomes based on clinical needs, as well as the current limitations and future directions of nanobiotechnology in the applications of ferroptosis, which will not only provide significant guidance for the clinical applications of ferroptosis and nanobiotechnology but also accelerate their clinical translations.
Keywords: Clinical treatment; Drug delivery; Drug resistance; Ferroptosis; Nanobiotechnology; Regulatory mechanism.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023M733022/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- GZB20230652/Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF
- 32201137/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82122076/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023578116/Youth Innovation Program of Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

