Evaluation of the therapeutic potential of novel nanoparticle formulations of glutathione and virgin coconut oil in an experimental model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver failure
- PMID: 39380023
- PMCID: PMC11460069
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-024-00795-x
Evaluation of the therapeutic potential of novel nanoparticle formulations of glutathione and virgin coconut oil in an experimental model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver failure
Abstract
Background: Acute liver failure (ALF) is a critical condition characterized by rapid liver dysfunction, leading to high mortality rates. Current treatments are limited, primarily supportive, and often require liver transplantation. This study investigates the potential of a novel nanoparticle formulation of glutathione (GSH) and virgin coconut oil (VCO) alone and in combination to enhance therapeutic outcomes in a rat model of ALF induced by orogastric carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
Methods: The study employed adult male Albino rats divided into ten groups, with ALF induced via a single oral dose of CCl4. Various treatment regimens were administered over seven days, including conventional and nanoparticle forms of GSH and VCO and their combinations. The efficacy of treatments was evaluated through biochemical analysis of liver function markers, oxidative stress indicators, inflammatory biomarkers, and histopathological examinations. Nanoparticles were synthesized using established methods, and characterization techniques were employed to ensure their quality and properties.
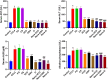
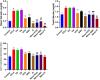
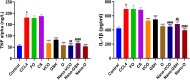
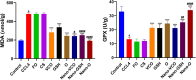
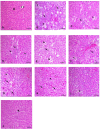
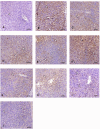
Results: The nanoparticle formulations significantly improved liver function, as indicated by reduced serum levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, alongside decreased oxidative stress markers such as malondialdehyde. Furthermore, they reduced tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta inflammatory markers. Histological analysis revealed reduced hepatocellular necrosis and inflammation in treated groups compared to controls. Also, decreased nuclear factor-kappa B was detected by immunohistochemical analysis.
Conclusion: The findings show that the nanoparticle mixture of GSH and VCO effectively reduces liver damage in ALF. This suggests a promising drug-based approach for improving liver regeneration and protection. This innovative strategy may pave the way for new therapeutic interventions in the management of ALF.
Keywords: ALF; Carbon tetrachloride; IL-1β; NF-κB; Nanoparticles; VCO.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The involvement of Nrf2 in the protective effects of diallyl disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage and inflammatory response in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:174-85. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24246655
-
Zerumbone Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and the Inflammatory Response: Involving the TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 Pathway.Molecules. 2019 May 22;24(10):1964. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101964. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31121820 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pharmacological strategy using nanoparticles with glutathione and virgin coconut oil to treat gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;398(1):933-950. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03303-4. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39093465 Free PMC article.
-
Phycocyanobilin accelerates liver regeneration and reduces mortality rate in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 14;21(18):5465-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5465. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25987768 Free PMC article.
-
The Hepatoprotective Effect of Selenium-Enriched Yeast and Gum Arabic Combination on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Chronic Liver Injury in Rats.J Food Sci. 2018 Feb;83(2):525-534. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14030. Epub 2018 Jan 19. J Food Sci. 2018. PMID: 29350750
Cited by
-
A novel nanoparticle glutathione and Lepidium sativum treatment for gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 20;15(1):20158. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05385-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40542040 Free PMC article.
-
A Literature Review of Glutathione Therapy in Ameliorating Hepatic Dysfunction in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 6;13(3):644. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030644. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Preserving Mitochondrial Dynamics Balance and Calcium Homeostasis.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Apr;197(4):2713-2733. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-05141-9. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39792339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong V, Nanchal R, Karvellas CJ. Pathophysiology of Acute Liver failure. Nutr Clin Pract. 2020;35(1):24–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

