SSRI use during acute COVID-19 and risk of long COVID among patients with depression
- PMID: 39380062
- PMCID: PMC11462648
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03655-x
SSRI use during acute COVID-19 and risk of long COVID among patients with depression
Abstract
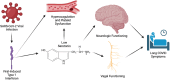
Background: Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), is a poorly understood condition with symptoms across a range of biological domains that often have debilitating consequences. Some have recently suggested that lingering SARS-CoV-2 virus particles in the gut may impede serotonin production and that low serotonin may drive many Long COVID symptoms across a range of biological systems. Therefore, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which increase synaptic serotonin availability, may be used to prevent or treat Long COVID. SSRIs are commonly prescribed for depression, therefore restricting a study sample to only include patients with depression can reduce the concern of confounding by indication.
Methods: In an observational sample of electronic health records from patients in the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) with a COVID-19 diagnosis between September 1, 2021, and December 1, 2022, and a comorbid depressive disorder, the leading indication for SSRI use, we evaluated the relationship between SSRI use during acute COVID-19 and subsequent 12-month risk of Long COVID (defined by ICD-10 code U09.9). We defined SSRI use as a prescription for SSRI medication beginning at least 30 days before acute COVID-19 and not ending before SARS-CoV-2 infection. To minimize bias, we estimated relationships using nonparametric targeted maximum likelihood estimation to aggressively adjust for high-dimensional covariates.
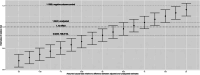
Results: We analyzed a sample (n = 302,626) of patients with a diagnosis of a depressive condition before COVID-19 diagnosis, where 100,803 (33%) were using an SSRI. We found that SSRI users had a significantly lower risk of Long COVID compared to nonusers (adjusted causal relative risk 0.92, 95% CI (0.86, 0.99)) and we found a similar relationship comparing new SSRI users (first SSRI prescription 1 to 4 months before acute COVID-19 with no prior history of SSRI use) to nonusers (adjusted causal relative risk 0.89, 95% CI (0.80, 0.98)).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that SSRI use during acute COVID-19 may be protective against Long COVID, supporting the hypothesis that serotonin may be a key mechanistic biomarker of Long COVID.
Keywords: COVID-19; Long COVID; SSRI.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests related to this study.
Figures

References
-
- Robertson MM, Qasmieh SA, Kulkarni SG, Teasdale CA, Jones HE, McNairy M, et al. The epidemiology of long coronavirus disease in US adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2023;76(9):1636–45. - PubMed
-
- Belluck P. Scientists offer a new explanation for long COVID. The New York Times. 2023. Available from: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/10/16/health/long-covid-serotonin.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR002649/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001860/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104942/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003096/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004556/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104938/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002537/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001412/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001872/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002529/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002494/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002736/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002369/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002541/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115371/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002001/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002538/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004406/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115458/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH131542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002535/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003167/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001409/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001449/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001453/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002489/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104940/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003107/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003015/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002733/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 TR002306/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001876/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001436/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002553/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002389/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001414/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104941/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002014/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002550/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002319/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001855/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002373/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002240/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002556/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003017/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001998/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002645/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002366/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115428/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002377/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115677/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002544/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003098/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

