Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke
- PMID: 39380217
- PMCID: PMC11462533
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240828.008
Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke
Abstract
Objective: To systematically evaluate the role of electroacupuncture in maintaining brain plasticity in ischemic stroke mediated brain damage.
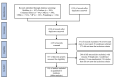
Methods: We searched for all relevant trials published through Oct 7, 2022 from seven databases. Metho-dological quality was assessed using the CAMARADES Risk of Bias Tool. A Meta-analysis of comparative effects was performed using Review Manager v.5.3 software.
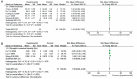
Results: A total of 101 studies involving 2148 animals were included. For most studies, primary outcomes results of the Meta-analysis indicate that EA significantly improved ischemic stroke rat's postsynaptic density thickness [Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) = 1.41, 95% confidence interval (CI) (0.59, 2.23), P = 0.0008], numerical density of synapses [SMD = 1.55, 95% CI (0.48, 2.63), P = 0.005] compared with non-EA-treated. Similarly, EA could improve parts of biomarkers of synapses, neurogenesis, angiogenesis and neurotrophin activity than the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The existing evidence suggests EA regulating ischemic stroke may be through brain plasticity. More rigorous and high quality studies should be conducted in the future.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; animal; brain plasticity; electroacupuncture; experimental ischemic stroke; systematic review.
Figures
References
-
- Srivastava A, Srivastava P, Verma R. Role of bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) in neurovascular interactions during stroke. Neurochem Int 2019; 129: 104480. - PubMed
-
- Datta A, Sarmah D, Mounica L, et al.. Cell death pathways in ischemic stroke and targeted pharmacotherapy. Transl Stroke Res 2020; 11: 1185-202. - PubMed
-
- Wang S, Lin B, Lin G, et al.. Automated label-free detection of injured neuron with deep learning by two-photon microscopy. J Biophotonics 2020; 13: e201960062. - PubMed
-
- Yuan L, Sun S, Pan X, et al.. Pseudoginsenoside-F11 improves long-term neurological function and promotes neurogenesis after transient cerebral ischemia in mice. Neurochem Int 2020; 133: 104586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

