Quality by design for mRNA platform purification based on continuous oligo-dT chromatography
- PMID: 39380714
- PMCID: PMC11458983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102333
Quality by design for mRNA platform purification based on continuous oligo-dT chromatography
Abstract
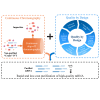
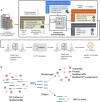
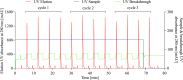
Oligo-deoxythymidine (oligo-dT) ligand-based affinity chromatography is a robust method for purifying mRNA drug substances within the manufacturing process of mRNA-based products, including vaccines and therapeutics. However, the conventional batch mode of operation for oligo-dT chromatography has certain drawbacks that reduce the productivity of this process. Here, we report a new continuous oligo-dT chromatography process for the purification of in vitro transcribed mRNA, which reduces losses, improves the efficiency of oligo-dT resin use, and intensifies the chromatography process. Furthermore, the quality by design (QbD) framework was used to establish a design space for the newly developed method. The optimization of process parameters (PPs), including salt type, salt concentration, load flow rate and mRNA load concentration both in batch and the continuous mode, achieved a greater than 90% yield (mRNA recovery) along with greater than 95% mRNA integrity and greater than 99% purity. The productivity of continuous chromatography was estimated to be 5.75-fold higher, and the operating cost was estimated 15% lower, when compared with batch chromatography. Moreover, the QbD framework was further used to map the relationship between critical quality attributes and key performance indicators as a function of critical process parameters and critical material attributes.
Keywords: Continuous manufacturing; MT: Delivery Strategies; mRNA therapeutics; mRNA vaccines; multi-column continuous chromatography process; oligo-dT affinity chromatography; quality by design.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Supercoiled DNA percentage: A key in-process control of linear DNA template for mRNA drug substance manufacturing.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 May 20;35(2):102223. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102223. eCollection 2024 Jun 11. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 38948330 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer of a three step mAb chromatography process from batch to continuous: Optimizing productivity to minimize consumable requirements.J Biotechnol. 2017 Jan 20;242:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.12.005. Epub 2016 Dec 6. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27939321
-
A rapid and efficient purification of poly(A)-mRNA by oligo(dT)30-Latex.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1988;(19):61-4. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1988. PMID: 2906428
-
Bacteriophage RNA polymerases: catalysts for mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Nov 21;11:1504876. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1504876. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39640848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatography bioseparation technologies and in-silico modelings for continuous production of biotherapeutics.J Chromatogr A. 2020 Sep 13;1627:461376. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461376. Epub 2020 Jun 29. J Chromatogr A. 2020. PMID: 32823091 Review.
References
-
- Whitley J., Zwolinski C., Denis C., Maughan M., Hayles L., Clarke D., Snare M., Liao H., Chiou S., Marmura T., et al. Development of mRNA manufacturing for vaccines and therapeutics: mRNA platform requirements and development of a scalable production process to support early phase clinical trials. Transl. Res. 2022;242:38–55. doi: 10.1016/J.TRSL.2021.11.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

