The genome sequence of Blair's Shoulder-knot, Lithophane leautieri (Boisduval, 1829)
- PMID: 39381070
- PMCID: PMC11459115
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.22610.1
The genome sequence of Blair's Shoulder-knot, Lithophane leautieri (Boisduval, 1829)
Abstract
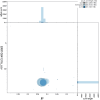
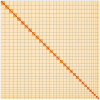
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Lithophane leautieri (Blair's Shoulder-knot; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). The genome sequence is 521.7 megabases in span. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into 31 chromosomal pseudomolecules, including the Z sex chromosome. The mitochondrial genome has also been assembled and is 15.4 kilobases in length. Gene annotation of this assembly on Ensembl identified 12,254 protein coding genes.
Keywords: Blair’s Shoulder-knot; Lepidoptera; Lithophane leautieri; chromosomal; genome sequence.
Copyright: © 2024 Lees DC et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures



References
-
- Bretherton RF, Goater B, Lorimer RI: Noctuidae (continued).In: Heath, J. and Emmet, A. M. (eds.) The Moths and Butterflies of Great Britain and Ireland, Vol. 10 Noctuidae (Cucullinae to Hypeninae) and Agaristidae.London: Curwen Books,1983;36–402.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

