Degenerate Two-Photon Rydberg Atom Voltage Reference
- PMID: 39381144
- PMCID: PMC11459451
- DOI: 10.1116/5.0090892
Degenerate Two-Photon Rydberg Atom Voltage Reference
Abstract
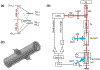
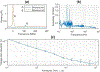
We implement a DC voltage reference by measuring Stark shifts of cesium Rydberg atoms in a vapor cell. Cesium atoms are excited from the ground state to the 15s state via a degenerate two-photon transition that provides a narrow, Doppler free line. The 15s state experiences a scalar, quadratic stark shift which is used to measure the voltage across a parallel plate capacitor integrated into the vapor cell. We demonstrate a sensitivity of at a bias voltage of 100 V. The device could be adapted for even larger voltages by increasing the plate spacing or using a lower energy state.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHOR DECLARATIONS The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
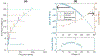
References
-
- Fan H, Kumar S, Sedlacek J, Kübler H, Karimkashi S, and Shaffer JP, “Atom based RF electric field sensing,” Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 48, 202001 (2015).
-
- Meyer DH, Castillo ZA, Cox KC, and Kunz PD, “Assessment of Rydberg atoms for wideband electric field sensing,” Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 53, 034001 (2020).
-
- Mohapatra AK, Bason MG, Butscher B, Weatherill KJ, and Adams CS, “A giant electro-optic effect using polarizable dark states,” Nature Physics 4, 890–894 (2008).
-
- Daschner R, Ritter R, Kübler H, Frühauf N, Kurz E, Löw R, and Pfau T, “Fabrication and characterization of an electrically contacted vapor cell,” Optics Letters 37, 2271–2273 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Barredo D, Kübler H, Daschner R, Löw R, and Pfau T, “Electrical readout for coherent phenomena involving Rydberg atoms in thermal vapor cells,” Physical Review Letters 110, 123002 (2013). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
